Published Date 22nd Dec, 2025
The eCommerce industry is entering a new phase of maturity, with multi-vendor marketplaces emerging as the dominant force driving this evolution. What started as large, generalized online malls has now transformed into highly specialized digital ecosystems that allow businesses, creators, wholesalers, and consumers to transact efficiently and at scale.
In 2026, multi-vendor marketplaces are no longer just “online stores with multiple sellers.” They are sophisticated platform businesses built on advanced technology, data intelligence, logistics, and community trust. From global retail giants to niche vertical platforms, marketplaces are dominating how commerce is built, scaled, and monetized worldwide.
In this blog, you will explore why multi-vendor marketplaces dominate eCommerce in 2026, highlight the top 30 platforms shaping global digital commerce, examine the business models driving marketplace success, identify high-potential niches for new founders, and explain how to build a scalable, future-ready marketplace powered by Yo!Kart.
Table of Contents
- Why Multi-Vendor Marketplaces Dominate in 2026
- Best 30 Multi-Vendor eCommerce Marketplaces to Watch in 2026
- What Marketplace Models Does this List Cover?
- Why this Matters for Marketplace Founders
- Looking to Build a Multi-Vendor eCommerce Marketplace?
- Yo!Kart Clients: Marketplaces Built Across Industries & Geographies
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Multi-Vendor Marketplaces Dominate in 2026?
The rise of multi-vendor marketplaces is not accidental. It is driven by structural advantages that traditional eCommerce stores struggle to match in terms of scale, speed, and sustainability. Further, given below are the reasons that clarify why multi-vendor marketplaces dominate in 2026:
1. Asset-Light, High-Growth Business Model
Unlike inventory-based eCommerce, marketplaces do not own or manage products. Vendors manage sourcing, pricing, and fulfillment, while the platform focuses on high-impact areas, such as:
- Technology and performance stability
- Seller onboarding
- Customer experience and support
- Secure payments and trust
This significantly reduces capital risk and enables rapid expansion without inventory bottlenecks.
2. Faster Time-to-Market Across Categories
A marketplace can expand into new categories simply by onboarding new sellers instead of building inventory from scratch. In 2026, speed is a major competitive advantage, and marketplaces outperform single-brand stores by launching and validating new product segments quickly.
3. Platform Economics & Network Effects
Marketplaces benefit strongly from network effects:
- More sellers → more product variety
- More buyers → higher seller revenue
- Higher activity → better data and personalization
Once momentum builds, growth compounds organically, making marketplaces increasingly defensible long-term businesses.
4. Multiple Monetization Opportunities
Unlike traditional eCommerce stores that rely only on margins, marketplaces generate revenue through multiple streams, such as:
- Commission per transaction
- Seller subscriptions plans
- Sponsored listings
- Advertising placements
- Logistics or fulfillment services
- Premium seller tools
This diversified revenue structure increases profitability, reduces dependency on a single income source, and strengthens long-term business resilience.
5. Consumer Preference for Choice & Trust
In 2026, customers prioritize convenience, transparency, and reliability. Buyers actively look for:
- Price comparison
- Verified seller reviews
- Fast and flexible delivery options
- One-stop shopping
Marketplaces bring all of this in one place, making them the preferred destination for modern consumers.
Best 30 Multi-Vendor eCommerce Marketplaces to Watch in 2026
Multi-vendor marketplaces continue to define how digital commerce is built and scaled globally. From mass-market retail platforms to niche, category-focused ecosystems, these marketplaces demonstrate how technology, logistics, and trust-driven models come together to create sustainable growth. Below is a curated list of the most influential multi-vendor marketplaces shaping eCommerce in 2026 across industries and regions:
Niche: Global & General Marketplaces
1. Amazon
Amazon is the world’s largest multi-vendor marketplace, enabling millions of sellers to reach global consumers. Its powerful logistics, fulfillment services, and AI-driven personalization make it a benchmark for scalable, high-volume eCommerce operations.
Key Highlights
- AI-powered search and recommendations
- Fulfillment-as-a-service (FBA)
- Advanced seller analytics
Supported Business Model
- B2C
- Hybrid (Platform + First-party retail)
2. eBay
eBay is a pioneer in online marketplaces, best known for resale, refurbished, and collectibles. It connects buyer-seller through auction and fixed-price listings, supported by strong trust, ratings, and buyer protection systems.
Key Highlights
- Auction and fixed-price selling
- Global peer-to-peer reach
- Strong resale ecosystem
Supported Business Model
- C2C
- B2C
Start Your Entrepreneurial Journey by Launching Your Own Multi-Vendor Marketplace
3. Walmart Marketplace
Walmart Marketplace allows third-party sellers to tap into Walmart’s vast retail ecosystem. With omnichannel capabilities and strict quality controls, it offers sellers access to millions of value-driven customers across online and offline touchpoints.
Key Highlights
- Online-offline integration
- Strict seller quality controls
- Competitive pricing focus
Supported Business Model
- B2C
4. Alibaba
Alibaba serves as a global B2B marketplace connecting manufacturers, exporters, and wholesalers with businesses worldwide. It plays a critical role in international trade by enabling bulk sourcing, supplier verification, and large-scale procurement.
Key Highlights
- Bulk buying and trade assurance
- Supplier verification systems
- Global sourcing at scale
Supported Business Model
- B2B
- B2B2C
5. AliExpress
AliExpress allows small and medium sellers to sell directly to international consumers. Known for affordable pricing and cross-border shipping, it helps sellers expand globally while giving buyers access to a vast and diverse product catalog.
Key Highlights
- Global shipping reach
- Affordable product discovery
- Seller-driven catalog expansion
Supported Business Model
- B2C
6. Rakuten
Rakuten is a Japanese marketplace ecosystem that blends eCommerce, fintech, and loyalty programs. Its seller-centric approach and rewards-driven model create strong customer retention while offering merchants tools to build long-term buyer relationships.
Key Highlights
- Loyalty rewards integration
- Fintech-powered ecosystem
- Seller-centric marketplace
Supported Business Model
- B2C
7. Mercado Libre
Mercado Libre is Latin America’s largest marketplace, offering payments, logistics, and financing within a centralized hub. It enables individuals and businesses to sell efficiently while addressing regional infrastructure challenges through its end-to-end commerce ecosystem.
Key Highlights
- Integrated digital payments
- Strong SME adoption
- Emerging-market scalability
Supported Business Model
- B2C
- C2C
8. Shopee
Shopee is a mobile-first marketplace dominating Southeast Asia through gamification and social commerce. Its app-driven experience, seller incentives, and interactive features drive high engagement and frequent purchases among price-conscious consumers.
Key Highlights
- Mobile-native UX
- High seller engagement
- Social shopping features
Supported Business Model
- B2C
- C2C
9. Lazada
Lazada focuses on brand-led marketplace growth across Southeast Asia. Backed by a strong logistics infrastructure, it supports large brands and professional sellers looking to scale operations while maintaining quality control and consistent customer experiences.
Key Highlights
- Brand partnerships
- Logistics-heavy model
- Premium seller focus
Supported Business Model
- B2C
10. OnBuy
OnBuy positions itself as a fair and transparent marketplace for sellers. By avoiding competition with merchants and maintaining simple commission structures, it attracts businesses seeking predictable costs and a level playing field.
Key Highlights
- No competition with sellers
- Simple commission structure
- Rapid European growth
Supported Business Model
- B2C
Niche: Fashion, Lifestyle & Resale Marketplaces
11. Etsy
Etsy is a marketplace for handmade, vintage, and creative products. It empowers artisans and small businesses to reach buyers seeking unique products, supported by a strong community, trust-driven reviews, and niche discovery features.
Key Highlights
- Strong community-driven commerce
- Niche discovery engine
- High buyer trust
Supported Business Model
- C2C
- B2C
Want to Build an Etsy-like Marketplace
12. Farfetch
Farfetch connects luxury boutiques and brands with high-end global buyers worldwide. It delivers a premium marketplace experience through curated listings, luxury-focused logistics, and seamless cross-border shopping for designer fashion enthusiasts.
Key Highlights
- Luxury-focused logistics
- Boutique-to-consumer model
- Global fashion reach
Supported Business Model
- B2C
13. ASOS Marketplace
ASOS Marketplace enables independent fashion labels to reach a style-conscious, youth-driven customer base. It emphasizes trend-led discovery and curated seller onboarding, making it a launchpad for emerging labels and niche fashion sellers.
Key Highlights
- Curated seller onboarding
- Trend-focused marketplace
- Brand discovery platform
Supported Business Model
- B2C
14. Zalando
Zalando operates as a fashion-focused marketplace ecosystem across Europe. By combining data-driven personalization, seller logistics services, and a seamless user experience, it helps brands scale while maintaining high conversion and customer satisfaction rates.
Key Highlights
- Data-driven personalization
- Logistics services for sellers
- High conversion UX
Supported Business Model
- B2C
15. Poshmark
Poshmark blends social networking with resale commerce, creating a community-driven shopping experience. Sellers and buyers interact through social features, making discovery, resale, and peer engagement central to the platform’s success.
Key Highlights
- Social selling mechanics
- Peer-driven discovery
- Strong resale economy
Supported Business Model
- C2C
16. Depop
Depop is a Gen-Z-focused resale marketplace where fashion meets creator culture. With a mobile-first, visual interface, it enables influencers and individuals to sell curated fashion items through storytelling and social engagement.
Key Highlights
- Influencer-led selling
- Mobile-first design
- Visual commerce
Supported Business Model
- C2C
17. Vinted
Vinted focuses on circular fashion by enabling peer-to-peer resale with minimal seller fees. Its sustainability-first approach and simple selling experience have driven strong adoption across Europe among environmentally conscious consumers.
Key Highlights
- Sustainability-first model
- No seller commission
- Strong European adoption
Supported Business Model
- C2C
Niche: Grocery, Hyperlocal & Essentials
18. Instacart
Instacart aggregates multiple grocery retailers, enabling fast, local deliveries. Its logistics-driven model focuses on real-time inventory, last-mile fulfillment, and convenience for urban and suburban consumers.
Key Highlights
- Real-time inventory sync
- Multi-retailer aggregation
- Logistics-first platform
Supported Business Model
- B2C
- B2B2C
19. Amazon Fresh
Amazon Fresh is Amazon’s grocery-focused marketplace offering fresh produce, packaged foods, and household essentials with same-day or scheduled delivery. Integrated with Amazon Prime, it emphasizes convenience, technology-driven fulfillment, and wide product selection.
Key Highlights
- Prime ecosystem integration
- Advanced fulfillment infrastructure
- Broad grocery assortment
Supported Business Model
- B2C
20. Kroger Online Grocery
Kroger’s online grocery platform enables customers to order groceries for delivery or pickup from one of the largest supermarket chains in the US. It combines data-driven inventory planning with regional fulfillment centers to scale efficiently.
Key Highlights
- Data-driven grocery operations
- Store + warehouse hybrid fulfillment
- Strong regional presence
Supported Business Model
- B2C
- B2B2C
21. GoPuff
GoPuff is a US-based quick-commerce platform delivering snacks, groceries, and everyday essentials in minutes. It operates on a dark-store model, owning inventory and logistics to ensure ultra-fast delivery in densely populated cities.
Key Highlights
- Rapid delivery model
- Dark-store operations
- High-frequency purchases
Supported Business Model
- B2C
Niche: Home, Furniture & Specialty Retail
22. Wayfair
Wayfair is a home and furniture marketplace connecting manufacturers and suppliers directly with consumers. Its platform supports complex logistics, large catalogs, and product discovery tailored specifically for home-focused shopping needs.
Key Highlights
- Supplier-driven catalog
- Specialized delivery systems
- Home-focused UX
Supported Business Model
- B2C
23. Houzz
Houzz blends inspiration, professionals, and product marketplaces for home renovation and design. It attracts high-intent users by blending content, expert services, and commerce within a single integrated platform.
Key Highlights
- Content-led commerce
- Professional service integration
- High-intent buyers
Supported Business Model
- B2C
- Service Marketplace
24. IKEA
IKEA’s US digital platform extends its global furniture brand into an omnichannel marketplace experience. It combines standardized furniture assortments with regional fulfillment centers and in-store pickup to efficiently manage bulky item delivery.
Key Highlights
- Omnichannel furniture retail
- Flat-pack logistics efficiency
- Store-assisted fulfillment
Supported Business Model
- B2C
Niche: B2B & Vertical Marketplaces
25. Thomasnet
Thomasnet is a US-based B2B marketplace connecting industrial manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors with business buyers. It focuses on supplier discovery and lead generation, enabling long-term B2B relationships across manufacturing and industrial sectors.
Key Highlights
- Lead-driven B2B discovery
- Industrial & manufacturing focus
- Verified supplier listings
Supported Business Model
- B2B
26. Faire
Faire is a wholesale marketplace enabling independent retailers to source products directly from brands. With flexible payment terms and discovery tools, it simplifies B2B buying and supports small retailers globally.
Key Highlights
- Net payment terms
- Brand discovery
- Retailer-first model
Supported Business Model
- B2B
27. Reverb
Reverb is a niche marketplace for musicians, offering instruments, gear, and accessories. It serves a passionate community by combining category expertise, trust-focused listings, and buyer-seller transparency.
Key Highlights
- Category expertise
- Trust-focused listings
- Enthusiast-driven community
Supported Business Model
- C2C
- B2C
28. StockX
StockX operates as a verified resale marketplace for sneakers, collectibles, and streetwear. Its authentication-first model and market-driven pricing bring transparency and trust to high-demand, limited-supply products.
Key Highlights
- Authentication-first model
- Market-driven pricing
- Limited-supply commerce
Supported Business Model
- C2C
29. Pinkoi
Pinkoi supports Asian designers and creators by connecting them with global buyers seeking unique products. It emphasizes cross-border commerce, creative storytelling, and curated discovery for niche, artistic goods.
Key Highlights
- Creator-led commerce
- Cross-border focus
- Design-first discovery
Supported Business Model
- C2C
- B2C
30. Carousell
Carousell is a mobile-first resale and classifieds marketplace popular across the Asia-Pacific region. Its simple listing process and community-driven transactions make peer-to-peer buying and selling fast and accessible.
Key Highlights
- Simple listing experience
- Community-driven transactions
- Strong mobile adoption
Supported Business Model
- C2C
What Marketplace Models Does this List Cover?
The multi-vendor marketplaces featured in this list represent a wide range of marketplace business models, each built to solve different commercial challenges and user needs. In 2026, successful marketplaces are no longer one-dimensional. They are hybrid, flexible, and often multi-model platforms.
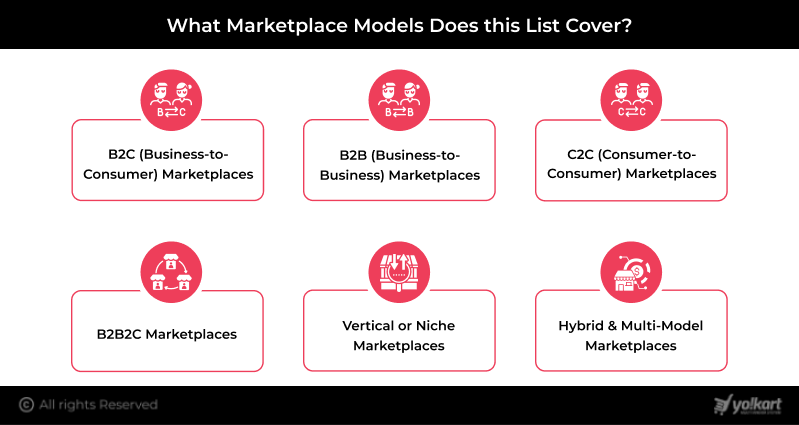
Below is a closer look at the primary marketplace models covered in this list and how they operate in today’s digital economy:
1. B2C (Business-to-Consumer) Marketplaces
B2C marketplaces enable brands, manufacturers, and professional sellers to sell directly to end consumers through a centralized platform. The marketplace acts as a facilitator by managing product discovery, trust, payments, and often logistics and fulfillment.
Why B2C Marketplaces Work in 2026?
- High consumer trust and convenience
- Scalable seller onboarding
- Strong control over quality and customer experience
Common Revenue Streams
- Commission per order
- Seller subscription plans
- Sponsored product placements
Examples from This List
Amazon, Walmart Marketplace, Wayfair, Zalando
2. C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer) Marketplaces
C2C marketplaces allow individuals to sell directly to other individuals, commonly focusing on resale, collectibles, handmade goods, or secondhand products. These platforms thrive on simplicity, community trust, ease of listing, and social engagement.
Why C2C Marketplaces Are Growing?
- Rising resale and circular economy trends
- Low entry barriers for sellers
- Community-driven commerce
Key Platform Requirements
- Robust ratings and reviews
- Dispute resolution mechanisms
- Secure payment escrow
Examples from This List
eBay, Etsy, Poshmark, Depop, Vinted, Carousell
3. B2B (Business-to-Business) Marketplaces
B2B marketplaces connect manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, and service providers with business buyers. Transactions are often high-value, repeat-driven, and built around long-term supplier relationships rather than one- time purchases.
Why B2B Marketplaces Are Booming?
- Ongoing digital transformation of procurement
- Increasing demand for global sourcing
- Greater efficiency in price discovery and supplier verification
Typical Monetization Models
- Lead-based pricing
- Subscription plans
- Transaction-based commissions
Examples:
Alibaba, IndiaMART, Faire
Launch a Marketplace Tailored to Your Niche
4. B2B2C (Business-to-Business-to-Consumer) Marketplaces
This hybrid model enables businesses to sell through intermediaries, such as local retailers, partners, or service providers, before reaching end consumers. It’s especially popular in industries where local presence, speed, and logistics efficiency are critical.
Why B2B2C Works in 2026?
- Bridges offline and online commerce
- Leverages existing local supply and retail networks
- Improves last-mile delivery efficiency
Core Use Cases
- Grocery delivery
- Hyperlocal retail
- Local store digitization
Examples:
Instacart, Mercado Libre
5. Vertical or Niche Marketplaces
Vertical marketplaces focus on one category, industry, or audience, offering depth instead of breadth. These platforms succeed by delivering highly specialized experiences, category expertise, and stronger trust compared to general-purpose marketplaces.
Why Vertical Marketplaces Outperform General Platforms?
- Higher user intent and purchase readiness
- Better conversion rates due to focused offerings
- Stronger community engagement and loyalty
Successful Vertical Strategies
- Category-specific filters and workflows
- Expert content and education
- Tailored seller onboarding
Examples:
StockX , Reverb, Houzz, Pinkoi
6. Hybrid & Multi-Model Marketplaces
Many leading platforms in 2026 operate as hybrid marketplaces, combining multiple business models within a single ecosystem. This flexibility allows them to diversify revenue, attract broader seller groups, and adapt quickly to changing market dynamics.
Benefits of Hybrid Models
- Broader seller participation across use cases
- Multiple monetization channels within one platform
- Greater resilience to demand and market shifts
Examples
Amazon, eBay, Houzz
Why this Matters for Marketplace Founders
Understanding these marketplace models before launch is critical for long-term success. The model you choose directly shapes how your platform is built, operated, and scaled. It influences key decisions across both technology and business operations, including:
- Platform architecture and feature design
- Monetization or revenue strategy
- Seller onboarding and management workflow
- Compliance requirements and operational complexity
Many modern marketplace solutions, including Yo!Kart is designed to support multiple business models simultaneously. This allows founders to start with a focused approach, validate demand, and expand into new models or categories over time without rebuilding their marketplace from scratch.
Looking to Build a Multi-Vendor eCommerce Marketplace?
Launching a multi-vendor marketplace in 2026 is no longer just about putting multiple sellers on one website. It requires scalable digital foundation that supports sellers, buyers, operations, and long-term growth from day one.
While the opportunity is massive, success depends heavily on the foundation you choose. From technology architecture to monetization flexibility, every decision made at the early stage determines how well your marketplace scales in the long run. Further, below are the steps to create a multi-vendor eCommerce marketplace:

Step 1: Define Your Marketplace Vision and Niche
Before choosing technology or design, establish clarity around your marketplace fundamentals. Hence, you should define:
- Who your sellers are (individuals, brands, manufacturers, service providers) and how they operate
- Who your buyers are (consumers, businesses, communities) and what problems they want solved
- The unique value your marketplace offers compared to existing platforms
In 2026, marketplaces that succeed are focused first, scalable later. Starting with a niche allows you to build trust, liquidity, and repeat usage before expanding into adjacent categories.
Step 2: Choose the Right Marketplace Business Model
Your marketplace business model determines transaction flows, revenue logic, and operational complexity.
Common models include:
- B2C for brand-led and professional selling
- C2C for peer-to-peer resale and community commerce
- B2B for wholesale and procurement platforms
- B2B2C for hyperlocal and logistics-driven platforms
Modern marketplaces often evolve into hybrid models over time, making it essential to choose a platform that supports multiple business models from the outset.
Step 3: Focus on Seller Experience From Day One
Marketplace growth depends on seller success. Platforms that invest early in seller experience build stronger supply, higher retention, and faster liquidity.
Key seller-centric capabilities to prioritize:
- Simple onboarding and KYC workflows
- Transparent commission and payout structures
- Dedicated seller dashboards
- Marketing and promotion tools
- Performance analytics and reporting
- Ratings, reviews, and dispute resolution systems
In 2026, sellers expect platforms to act as growth partners, not just listing directories.
Step 4: Design for Scale, Not Just Launch
Many marketplaces struggle because they are built for launch, not growth. Thus, scalability must be part of the platform architecture.
Your platform should support:
- Multi-currency and multi-language expansion
- High traffic and transaction volumes
- Third-party integrations, such as logistics, CRM, and ERP
- API-driven extensibility for future features
Scalability should be architectural, not an afterthought.
Step 5: Power Your Marketplace With the Right Technology
Using generic eCommerce platforms with plugins often leads to:
- Performance bottlenecks
- Feature limitations
- Complex workarounds
- Vendor lock-in
A purpose-built marketplace solution provides native support for:
- Multi-vendor workflows
- Commission management
- Vendor-specific catalogs
- Admin-level control and moderation
This significantly reduces technical debt and long-term costs.
One such purpose-built marketplace software is Yo!Kart is a self-hosted multi-vendor solution built specifically for founders who want control, flexibility, and scalability.
What sets Yo!Kart apart:
- Designed exclusively for marketplace businesses
- One-time license with full source-code ownership
- Highly customizable workflows
- Supports B2C, B2B, C2C, and niche marketplaces
- Scales from startup MVPs to enterprise-grade platforms
Instead of forcing your idea into a rigid framework, Yo!Kart adapts to your business vision, allowing you to evolve without rebuilding.
Book a Personalized Yo!Kart Demo
Step 6: From MVP to Full-Scale Marketplace
Most successful marketplaces follow a phased growth approach:
- Launch with a focused niche
- Achieve initial liquidity and trust
- Optimize seller and buyer experience
- Expand categories, regions, or business models
- Introduce advanced monetization layers
The right foundation helps you to scale the marketplace with ease. Hence, scaling becomes an extension of growth, not a technical challenge.
Building a successful multi-vendor marketplace is not just about technology—it’s about choosing a foundation that grows with your vision. This is where proven platforms make the difference. Over the years, Yo!Kart has empowered marketplace founders across industries to launch, scale, and evolve with confidence. Below, let’s explore how businesses worldwide are leveraging Yo!Kart to turn marketplace ideas into sustainable success stories.
Yo!Kart Clients: Marketplaces Built Across Industries & Geographies
Yo!Kart has been trusted by entrepreneurs, enterprises, and industry innovators to build scalable, domain-specific multi-vendor marketplaces. However, what differentiates these platforms apart is not just the technology, but how Yo!Kart adapts to diverse business models, regional requirements, and niche workflows.
The following examples highlight how Yo!Kart has powered marketplaces across a wide range of industries, demonstrating Yo!Kart’s and real-world applicability rather than repeating implementation details.
1. UNI Diamonds, Digital Transformation of the Diamond Trade
Industry: B2B Diamond Marketplace
UNI Diamonds represents how a traditionally trust-driven industry can successfully transition to digital commerce. The marketplace enables professional buyers and sellers to discover, compare, and transact high-value products in a structured digital environment. This use case highlights Yo!Kart’s ability to support secure B2B workflows, complex catalogs, and industry-specific compliance needs.
View Case Study
2. Voyij, Experiences & Activities Marketplace
Industry: Travel & Tourism
Voyij showcases Yo!Kart’s flexibility beyond physical products. The platform connects travelers with local experience providers, supporting time-based bookings, service listings, and vendor-managed availability. This marketplace reflects how Yo!Kart adapts to experience-led and service-oriented commerce models.
3. Watersorted, Infrastructure & Utility Marketplace
Industry: Water & Infrastructure (B2B)
Watersorted operates as a specialized procurement marketplace for water management solutions. This platform highlights Yo!Kart’s strength is in technical B2B environments, where buyers need structured product data, supplier discovery, and industry-focused navigation.
Explore More
4. Tajer, Regional Multi-Category Marketplace
Industry: Retail (Fashion, Electronics, Lifestyle)
Tajer is a multi-category marketplace tailored for a regional audience. It demonstrates Yo!Kart’s ability to support localized payment methods, regional shipping rules, and culturally aligned UX, while still operating at scale across multiple vendors and product categories.
Read Case Study
5. 4GoodVibes, Handmade & Creative Goods Marketplace
Industry: Handmade & Artisan Products
4GoodVibes represents a community-focused marketplace where independent creators sell unique handcrafted products. This platform emphasizes Yo!Kart’s suitability for creator economies, C2C commerce, and trust-based selling environments.
Conclusion
As we move into 2026, multi-vendor marketplaces are no longer optional. They have become the preferred model for building scalable and resilient digital commerce businesses across industries. Whether it’s global retail, B2B procurement, niche communities, or experience-driven platforms, marketplaces outperform traditional eCommerce by enabling faster growth without inventory risk, diversified monetization, and stronger network effects.
The success stories of leading marketplaces, along with platforms built using Yo!Kart highlights that the future belongs to businesses that enable ecosystems, not just transactions.
For founders and enterprises planning to enter this space, choosing the right marketplace software is not just a technical decision, but a strategic one that determines how effectively the marketplace scales, adapts, and competes in the long term.
FAQs
Q 1. What is a multi-vendor eCommerce marketplace?
Ans. A multi-vendor marketplace is an online platform where multiple independent sellers list and sell products or services through a shared storefront. The platform manages listings, payments, and trust, while sellers handle inventory and fulfillment, creating a scalable ecosystem for buyers and merchants.
Q 2. Is launching a marketplace still viable in 2026?
Ans. Yes, launching a marketplace in 2026 remains highly viable. While generic marketplaces are saturated, niche and vertical marketplaces continue to see strong growth due to focused demand and community-driven engagement. Moreover, they solve specific problems and build strong communities that encourage repeat usage and long-term loyalty.
Q 3. Which marketplace model is best for startups?
Ans. For startups, niche B2C, C2C, and service-based marketplaces work best due to lower competition and faster liquidity building. These models require lower upfront investment and achieve supply-demand balance faster, helping founders validate their idea and build trust without excessive operational complexity.
Q 4. Can one marketplace support multiple business models?
Ans. Yes, a single marketplace can support multiple business models. Modern marketplaces often evolve into hybrid models (e.g., B2C + C2C). Platforms like Yo!Kart isbuilt to support such flexibility, which mamakest possible to evolve without rebuilding the entire platform.
Q 5. Do I need technical expertise to run a marketplace?
Ans. No, you do not need deep technical expertise to run a marketplace. While custom development may require technical input, ready-made marketplace software significantly reduces development complexity and time-to-market. Additionally, it allows founders to focus more on growth, sellers, and customer experience.
Q 6. Why choose a self-hosted marketplace solution?
Ans. A Self-hosted marketplace solution offers full control over data, features, and scaling decisions. It allows deep customization, better scalability, and no vendor lock-in, making them ideal for long-term marketplace growth.