Published Date 21 Nov 2025
The multi-vendor eCommerce market is advancing at a mindboggling momentum, reflecting a spectacular growth at a CAGR of 18.9% from 2025-2030, while expecting to reach a splendid $83.26 trillion by 2030.
However, the real competitive edge no longer lies entirely in onboarding more vendors or expanding product catalogs. Today, the key distinguisher is the economic architecture behind the platform. This shift is prompting a deeper evaluation of business models, and thus subscription-based pricing models are swiftly moving to the forefront. Marketplaces seeking financial predictability and greater operational control are increasingly gravitating towards subscription-based models.
But, with this transition comes a critical question that if these subscription-based models are genuinely profitable in multi-vendor platforms.
Hence, this blog examines the strategic relevance of subscription-based models in multi-vendor platforms, how they operate and whether they’re really profitable in multi-vendor environments.
Table of Contents
- What is a Subscription-Based Model?
- How Does a Subscription-Based Model Work?
- Leading Players of Subscription-Based Marketplaces
- Key Features of a Subscription-Based eCommerce Marketplace
- Benefits of Adopting Subscription-Based Models
- Drawbacks of Recurring Revenue Models in Multi-Vendor Platforms
- Are Subscription-Based Models Profitable in Multi-Vendor Platforms?
- Top Alternative Monetization Models
- Best Software to Build a Subscription-Based Multi-Vendor Marketplace
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Subscription-Based Model?
Recurring subscription-based eCommerce marketplace models offer a versatile revenue model in which users pay a fixed, recurring fee, typically on a monthly, quarterly or annual basis, to access the multi-vendor platform. Instead of charging per transaction or per sale, users are made to purchase a membership plan to access the products or services on the platform.
While the vendors benefit from specialized offers and advanced features, buyers benefit from exclusive perks, specialized delivery services and more. Additionally, these models shift the users’ mindset from reactive cost payments to proactive value investment. Moreover, users commit to a definite cost structure that aligns with the perceived value.
How do Subscription-Based Models Differ From Traditional Business Models?
A subscription-based model deviates fundamentally from conventional revenue structures by replacing unpredictable, transaction-led earnings with a stable, recurring income stream. Unlike commission-based models where earnings depend solely on transaction volume, subscription costs monetize continued access and specialized benefits.
Moreover, subscription-based revenue structures can be influential for both sellers and customers in many ways. Additionally, this dual-sided structure strengthens revenue predictability for marketplace owners. Compared with listing fees or pay-per-sale model, subscription-based models consolidate a unified, value-driven offering that enhances the long-term growth of a multi-vendor platform.
| Parameters | Subscription-based Models | Traditional Business Models |
| Explanation | Users pay a fixed, recurring fee to access the platform and offerings | Users pay only for the items they purchase |
| Revenue Stream | Recurring & predictable due to ongoing costs | Fluctuating & unpredictable due to one-time transactions |
| Value Delivery | Essential to deliver continuous value to engage and retain users | Delivered at the time of purchase |
| Demand Forecasting | Generally simpler due to recurring subscription revenue | Comparatively difficult as the customer demands, expectations & seasonal patterns keep fluctuating |
| Customer Relationship | Focuses on prolonged & continuous customer retention | Focused essentially on one-time transactions |
How Does a Subscription-Based Model Work?
Unlike long-established marketplace revenue models, subscription-based models create a predictable recurring revenue stream for marketplace owners, ensuring long-term marketplace growth. Here’s how subscription-based models work:
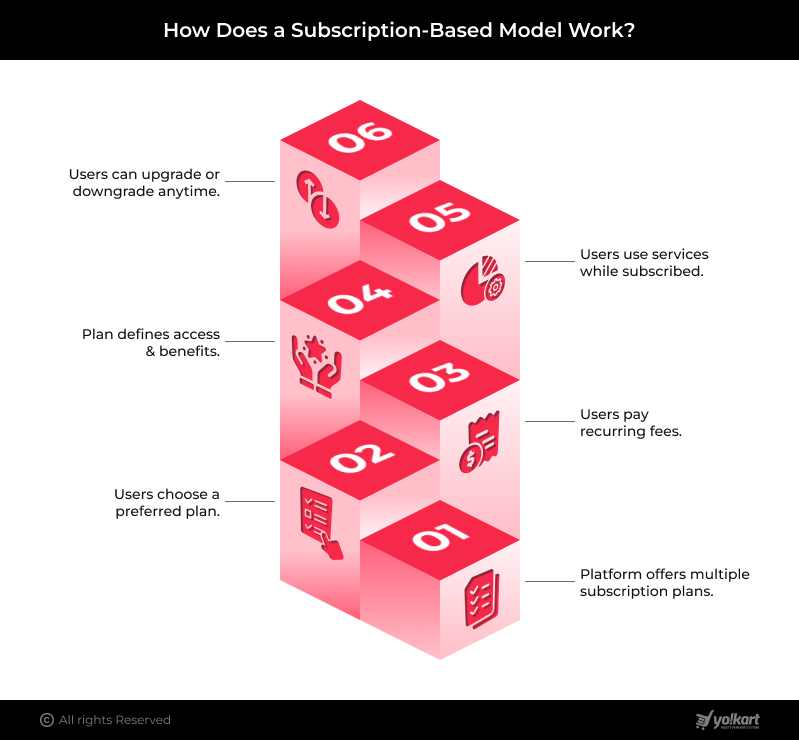
- The platform offers diverse subscription plans, each designed with different levels of functionalities and offerings.
- Users choose a subscription tier that they prefer.
- They pay a recurring fee, be it on a monthly, quarterly or an annual basis, to stay active on the platform.
- The chosen subscription tier determines the user’s operational capabilities and benefits.
- Users use the platform and obtain products/services for as long as their subscription remains active.
- Users can change their subscription tier to either higher or lower plans as per their requirements in the future.
Leading Players of Subscription-Based eCommerce Marketplaces
Subscription led marketplaces have earned a considerable amount of traction across both B2C and B2B environments. These platforms generate predictable recurring revenue while delivering sustained value to the users, modernizing traditional marketplace dynamics by replacing transactional uncertainty.
Here are some of the prominent marketplaces that deploy subscription models at scale:
1. Amazon:
Amazon is a globally recognized eCommerce marketplace launched in 1995. While primarily known for selling books online, the platform has now progressed in diverse regions such as eCommerce, digital streaming, online advertising, artificial intelligence and cloud computing. Similarly, its subscription-based models include exclusive benefits for both its sellers and customers, known as:
- Amazon Professional Seller Plans: Amazon’s Professional Seller tier exemplifies a high-performing subscription framework within a global marketplace. Rather than paying per item sold, sellers subscribe to a fixed monthly fee, offering advanced operational capabilities. This allows Amazon to maintain reliable recurring revenue while offering sellers a scalable cost structure.
- Amazon Prime Membership: Amazon Prime is a flagship example of subscription-based value creation. The membership’s bundled benefits, such as expedited delivery, digital media and exclusive deals, fuel a high-velocity purchasing ecosystem that benefits customers, sellers and marketplace operators as well.
2. Etsy Plus:
Etsy Plus, an American eCommerce marketplace for handmade or vintage products, represents a refined, value-driven subscription tier tailored for ambitious vendors seeking greater visibility and brand distinction. This subscription offers enhanced storefront customization, priority access to merchandising tools and discounted listing & advertising credits. Thus, by offering advanced capabilities into a monthly plan, Etsy cultivates a professional seller segment while maintaining a steady, recurring income channel.
3. Audible:
Audible is a US-based audiobook and podcast service eCommerce marketplace is fundamentally designed around a consumer subscription model. Members pay a recurring monthly fee in exchange for monthly credits and exclusive access to premium audio content. For creators and publishers, this model ensures consistent demand and predictable payouts, while customers benefit from curated listening experiences, creating a high-retention environment.
4. Thumbtack:
Thumbtack operates on a subscription-centric model for service professionals, offering them systematic access to high-intent customer leads. Instead of relying exclusively on commissions, Thumbtack employs recurring plans, ensuring predictable lead flow, positioning it as a dependable acquisition channel while securing robust, steady monthly revenue for the platform.
5. Envato Elements & StockX:
- Envato Elements epitomizes a subscription-first digital marketplace that offers customers unlimited access to curated creative assets under a monthly recurring payment.
- Conversely, StockX offers a Flex membership tier for its premium sellers to list and sell products at lower commissions.
Both these platforms demonstrate how subscriptions can be layered to amplify value while ensuring predictable, recurring revenue.
Planning to Build a Similar Multi-Vendor eCommerce Marketplace?
Essential Features to Launch a Subscription-Based eCommerce Marketplace
To build a multi-vendor eCommerce marketplace, the platform must integrate a robust suite of features specific to eCommerce operations. Hence, here’s a curated list of essential features required to launch a subscription-based eCommerce platform:
- Subscription Plan Management: Create flexible, multi-tiered subscription plans, reflecting clear differentiation in pricing, access privileges and benefits to support diverse monetization and engagement strategies.
- Role-based Access Controls: Assign platform permissions based on subscription tiers, enabling strategic feature gating that elevates premium value perception and naturally incentivizes tier upgrades.
- Vendor Onboarding & Verification: Streamline vendor registration with guided steps, compliance checks and seamless verification to establish a trustworthy, policy-aligned seller ecosystem on the platform.
- Automated Recurring Billing: Implement secure, automated billing cycles with multiple payment options, ensuring predictable, uninterrupted revenue flow while minimizing administrative overhead and enhancing payment reliability across global subscriber bases.
- Dedicated, Advanced Vendor Dashboards: Equip sellers with advanced dashboards featuring performance insights, product controls, subscription status and revenue analytics to drive operational clarity and data-led business growth.
- Products Listing Limits by Subscription Tiers: Define product upload caps, category access and listing privileges per tier, creating structured value differentiation that encourages sellers to upgrade for broader reach and more extensive selling capabilities.
- Buyer Subscription Tiers: Introduce structured customer memberships with clearly articulated benefits such as exclusive pricing, bonus rewards, priority service or faster delivery to strengthen loyalty and improve repeat purchase frequency.
- Exclusive Access & Early Access Features: Provide premium customers early access to discounts, collections, gated experiences or curated exclusives, strengthening perceived value and driving higher adoption of elevated membership plans.
- Marketing & Promotional Tools: Offer tactical promotional capabilities such as coupons, discounts, featured listings and outreach tools to empower sellers to enhance visibility and maximize returns from premium subscription tiers.
- Advanced Reports & Analytics: Deliver deep analytical visibility into subscription performance, user behavior, churn patterns, lifecycle metrics and platform earnings, enabling data-backed optimization of marketing campaigns and growth strategies.
- Integrated Payment Gateways: Ensure reliable, multi-currency payment processing with secure, global payment gateway compatibility, enabling smooth subscription purchases, renewals and upgrades across diverse customer & seller segments.
- Push Notifications: Send automated, timely alerts for subscription renewals, expirations, payment failures and upgrades, enhancing transparency while significantly reducing involuntary churn across the platform.
- Scalable, High-Performance Architecture: Deploy a performance-optimized, scalable infrastructure capable of handling large user bases, multiple locations, heavy subscription traffic and high transaction loads without compromising speed or user experience.
Key Benefits of Adopting Subscription-Based Models in Multi-Vendor Platforms
A subscription-based model delivers substantial benefits for multi-vendor platforms, especially those aiming for predictable growth, stronger vendor engagement and long-term customer loyalty. If executed properly, these subscriptions not only stabilize revenue but also enhance platform efficiency and user experience. Hence, here are the key benefits of adopting subscription-based models in multi-vendor platforms:
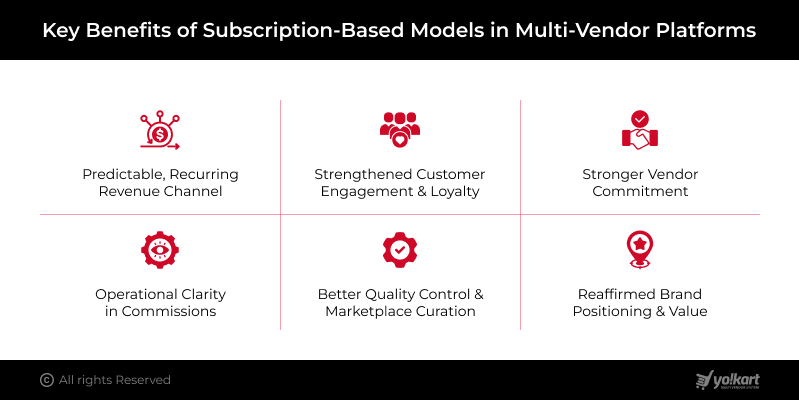
1. Predictable, Recurring Revenue Channel:
Subscription channels create a steady revenue stream that is largely independent of transactional volatility. This predictability enables more accurate financial forecasting, stronger cash-flow management and enhances the platform’s capacity to allocate resources with confidence. For marketplaces scaling globally or expanding into new verticals, a recurring revenue stream can become instrumental in supporting long-term growth and investment cycles.
2. Strengthened Customer Engagement & Loyalty:
Recurring plans, such as Amazon Prime’s membership tier, encourage repeat usage and reinforce brand affinity. Members are more likely to consolidate their purchases within the platform, increasing customer lifetime value. Moreover, curated benefits such as expedited delivery and exclusive discounts further create clear competitive differentiation, cultivating customer loyalty.
3. Stronger Vendor Commitment:
Sellers who pay a recurring subscription fee tend to demonstrate a higher degree of commitment to the platform. Subscription fees signal intentional investment, resulting in:
- More consistent product listings
- Improved service and fulfillment standards
- Proactive participation on the platform
This heightened commitment strengthens the marketplace’s overall supply-side stability and thus contributes to a more predictable, high-quality marketplace environment.
4. Operational Clarity in Contrast to Commissions:
In comparison to commission-based models, subscription plans offer simplicity and transparency, particularly attractive for high-volume or experienced sellers. Sellers benefit from transparent, fixed costs without concerns about diminishing margins as business scales, while customers benefit from exclusive perks, streamlined deliveries and more. Additionally, for the marketplace, this eliminates administrative overhead costs, streamlining operations and improving overall efficiency.
5. Better Quality Control & Marketplace Curation:
Subscription packages inherently filter out low-effort or low-quality sellers who are less likely to invest in maintaining platform standards, resulting in a more curated, trustworthy marketplace. This enhances buyer confidence and contributes to a more premium & professional ecosystem. Additionally, member-only access can help maintain higher engagement quality and reduce spam or fraudulent activities.
6. Reaffirmed Brand Positioning & Perceived Value:
A subscription proposition communicates enduring value, positioning the marketplace as a growth enabler rather than a transactional intermediary. Consistent delivery of premium features, exclusive tools or customer benefits strengthens the platform’s brand equity and frames the subscription as a strategic partnership.
Potential Drawbacks of Recurring Revenue Models in Multi-Vendor Platforms
Despite their ability to generate predictable recurring revenue, subscription-based models come with nuanced challenges that marketplace owners must weigh carefully. In multi-vendor ecosystems, an obstinate subscription strategy can introduce friction and operational risk.
Here are some of the common challenges that businesses must outweigh:
1. Heightened Entry Barriers for New Sellers:
A mandatory recurring fee can discourage new, small-scale sellers with limited budgets from onboarding. Unlike commission-based models that charge only when a sale is made, a subscription fee requires upfront financial commitment that can limit marketplace diversity and slows down early-stage seller acquisition.
2. Perceived Lack of Instant ROI:
Sellers often expect rapid and measurable returns, which is why, if the subscription does not translate into visibility, quality leads and incremental sales quickly, sellers may thus experience dissatisfaction. This can result in higher churn and negative sentiment that might compromise marketplace performance and reputation.
3. Inconsistency with Low-Volume or Seasonal Business Models:
Sellers with cyclical or inconsistent sales patterns may perceive subscription-based models as rigid and financially inefficient. Without a variable cost structure that mirrors their requirements, these sellers may opt for other competing platforms with more flexible pricing frameworks.
4. Pricing Sensitivity or Commercial Risk:
Determining an optimal subscription price is a delicate balancing act, because:
- Underpricing can erode profitability and dilute perceived value, struggling to cover operational costs
- On the contrary, overpricing can suppress user adoption and thus limit platform scalability
Price alignment is particularly risky in multi-vendor ecosystems where seller categories differ widely in margins, order value and sales value. Hence, implementing these costs demands higher precision and understanding.
5. Buyer Resistance and Subscription Fatigue:
On the consumer side, subscription fatigue is an increasingly notable trend nowadays. A customer who already pays for multiple streaming, shopping or delivery services may hesitate to adopt another subscription simply to access a marketplace. Hence, if not placed correctly, such fees can limit user acquisition and reduce marketplace traffic.
Adopt a Powerful Multi-Vendor Marketplace Software that Supports Diverse Monetization Models
Are Subscription-Based Models Profitable in Multi-Vendor Platforms?
A subscription-based model undeniably offers several operational and financial advantages, as highlighted in the earlier sections. It offers predictable revenue, stronger seller commitment and steadier financial planning. Yet, when these advantages are weighed against the broader landscape of marketplace dynamics, it becomes evident that relying solely on a single monetization model can create constraints over time.
A single business model, no matter how efficient, often performs well at the initial stages, but:
- It may restrict the platform’s flexibility as the marketplace matures. Different sellers incline toward different value propositions, and relying solely on a single revenue stream can thus leave potential earnings untapped.
- Competitive differentiation becomes hard to achieve when monetization lacks flexibility.
- Plus, certain product categories or seasonal sellers may find a single monetization model misaligned.
Hence, a diversified monetization structure creates a more balanced revenue mix and strengthens long-term profitability. In essence, while a subscription-based model is a strong strategic foundation, a multi-layered monetization strategy generally positions a multi-vendor platform for more resilient long-term profitability.
Top Alternative Monetization Models in Multi-Vendor Platforms
While subscription-based pricing delivers predictable recurring revenue, multi-vendor eCommerce platforms often benefit from diversifying their monetization channels. Broadening the revenue channels not only enhances financial resilience but also empowers the marketplace to serve a broad spectrum of users. Thus, the following models represent the most strategically relevant alternatives or complements to subscription-based monetization:
- Sales: It is the most straightforward model in which the platform generates revenue directly from sales of goods and services itself, getting the entire rental fee.
- Commissions: A foundational model for many marketplaces that allows admins to levy commissions per transaction made through the platform as a platform commission.
- Listing Fee: This allows marketplace owners to charge vendors a fixed cost to publish products or services on the platform to make sure only the serious and dedicated sellers join, discouraging spam and low-value listings.
- Advertising: Generate substantial income by offering paid advertising slots to third-party businesses on your marketplace, generating an additional revenue stream from clicks or conversions.
- Partnerships: Partner with local businesses for cross-promotions and exclusive brand visibility, unlocking co-branded offerings, revenue sharing and expanding distribution channels.
- Featured Listings: Premium visibility packages allow vendors to pay for prioritized visibility on premium pages of the marketplace such as top sections, curated collections or spotlight placements.
- Value-Added Services: Offer premium services or complementary products with the main products to increase the overall cart value, catering to customers seeking special services.
- Hybrid Model: Most leading multi-vendor eCommerce marketplaces adopt a hybrid monetization strategy, strategically blending the above-mentioned revenue streams, ensuring revenue stability.
Yo!Kart — Best Software to Build a Subscription-Based Multi-Vendor eCommerce Marketplace
Yo!Kart, a product of FATbit Technologies, stands out as an enterprise-grade multi-vendor eCommerce marketplace software engineered specifically for multi-vendor eCommerce platforms seeking scalable monetization. Meticulously crafted with precision, the software offers a powerful combination of flexibility, performance and scalability.
At its core, Yo!Kart provides a highly configurable framework that allows businesses to adapt to varied business models and requirements. The software provides advanced vendor management capabilities, automated billing & invoicing, granular access controls, integrated marketing tools and analytics that unveil profitability at every step. Additionally, Yo!Kart is built to support businesses of all sizes from startups and small businesses to mid-sized businesses and large enterprises, accommodating large vendor bases and increasing transactions without compromising performance.
Besides, with lifetime ownership, extensive customization capabilities, robust security frameworks and proven performance across marketplaces at scale, Yo!Kart enables businesses to launch and expand multi-vendor marketplaces confidently.
Additional Benefits of Yo!Kart:
- 100% white label software
- Self-hosted solution with one-time upfront pricing
- Lifetime license, no recurring charges
- Over 10 years of industry expertise
- Extensively scalable and secure
- Highly customizable, modular framework
- Expansive suite of multi-vendor marketplace features
- Adaptable, API-driven infrastructure
- 1 year free technical support post-purchase
Yo!Kart Supported Business Models & Marketplaces Built in that Space:
| Business Models | Industry Giants | Yo!Kart Powered Marketplaces |
| Subscription-based | Amazon Prime, Etsy Plus | All marketplaces built with Yo!Kart support a subscription-based revenue model |
| B2C (Business-to-Consumer) | Amazon, Walmart, eBay | Voyij, Tajer, 4GoodVibes, RxAll, etc. |
| B2B (Business-to-Business) | Alibaba, Amazon Business, Global Sources | UNI Diamonds, WaterSorted, Bozinga, Anyflexo, etc. |
| P2P (Peer-to-Peer) | Etsy, Poshmark, eBay | WeDIY, Iconic Motorbikes |
| Hyperlocal Platforms(connects buyers with local sellers) | OLX, OfferUp, InstaCart | Little Local, Shop American Sellers, Glocal Store, DotDune |
| Commission-Based | Amazon, Etsy, eBay | All marketplaces built with Yo!Kart support a commission-based model |
| Niche/Vertical Marketplaces | Newegg, ASOS, Zalando, GNC | Clic & Pick, Party Without Plastic, TransporTECO, Sandhai, Canna Market, CBD Supplements, etc. |
Navigate the Yo!Kart’s clients page to get more information about the marketplaces built with Yo!kart.
Book a Free Personalized Demo Session to Explore Yo!Kart Firsthand
Conclusion
Subscription-based models have today evolved from optional revenue add-ons to strategic growth levers for modern multi-vendor eCommerce platforms. As consumer behavior shifts towards convenience and predictable value, and sellers increasingly seek stability and enhanced platform services, subscriptions offer marketplaces a strong passage to recurring revenue and deeper engagement. However, profitability rarely lies in counting on a single monetization model. Hence, the most resilient, future-ready multi-vendor eCommerce platforms must blend subscriptions with complementary monetization strategies such as commissions, sales, advertisements or hybrid structures to create a balance and build a scalable multi-vendor eCommerce marketplace.
FAQs
Q 1. What are subscription-based models?
Ans. Subscription-based models are monetization models that involve a recurring subscription fee for users to access the marketplaces and get exclusive benefits. These models create a predictable revenue stream for marketplace owners while strengthening the platform engagement and loyalty.
Q 2. Are subscription-based models profitable in multi-vendor marketplaces?
Ans. Subscription-based revenue models offer a stable and predictable revenue channel for marketplaces, improving vendor retention and elevating customer lifetime value. However, relying solely on a single monetization model may limit growth potential. Thus, combining multiple business models offers a more strategic foundation for sustainable growth.
Q 3. Does Yo!Kart support subscription-based marketplaces?
Ans. Absolutely. Yo!Kart offers in-built capabilities for tiered subscription plans, recurring fee renewals, feature-based access controls, value-based privileges and robust analytics tools, allowing marketplace owners to manage and optimize subscription monetization easily.
Q 4. Can I customize Yo!Kart to support my unique business model?
Ans. Yes. Yo!Kart is built with a modular, highly customizable architecture that allows extensive customization to perfectly align with diverse business models, operational requirements, industry-specific demands and business vision. It offers the flexibility to tailor UI/UX, features and workflows to reflect your unique brand identity.