eCommerce has evolved far beyond simply selling products online; it’s now a dynamic ecosystem fueling global trade, innovation, and customer expectations. As businesses of all sizes increasingly shift their operations online, selecting the right eCommerce business model is a strategic decision.
The model you adopt directly influences how you attract customers, generate revenue, manage logistics, and scale your eCommerce business operations. Clarity on this front lays the foundation for sustainable growth, competitive differentiation, and operational efficiency.
Whether you’re entering new markets, re-evaluating your digital strategy, or refining your value proposition, understanding the distinctions between different eCommerce business models is essential. Each business model presents unique advantages, challenges, and alignment opportunities depending on your product type, audience, and goals.
In this blog, we’ll understand the different types of eCommerce business models to help you identify the structure that aligns with your strategic business goals.
Table of Contents
- Importance of Choosing the Right eCommerce Business Model
- The Core eCommerce Business Models
- Smart eCommerce Fulfillment Models Transforming Online Retail
- How to Choose the Right eCommerce Business Model?
- Which eCommerce Business Model is Popular in 2025?
- Best eCommerce Marketplace Software to Build a Thriving Marketplace
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Importance of Choosing the Right eCommerce Business Model
A clear, well-aligned eCommerce business model is essential for building a scalable, customer-centric eCommerce marketplace. It shapes how a platform delivers value, aligns internal resources, and competes in an increasingly saturated online market. Without a clear business model, businesses risk inefficiencies, misaligned strategies, and missed growth opportunities.
Here’s why choosing the right eCommerce business model is essential:
1. Strategic Foundation: A well-defined eCommerce business model provides the structural and strategic blueprint of how a business creates and delivers value. It aligns your core operations with long-term business objectives and revenue generation strategies, ensuring cohesive, goal-oriented growth.
2. Operational Clarity: A strategic business model brings consistency and direction to your day-to-day eCommerce business operations. It guides decisions related to inventory management, shipping logistics, and vendor relationships, improving efficiency, reducing friction, and enabling better performance tracking and continuous optimization.
3. Competitive Advantage: A distinct and purpose-driven business model helps you differentiate from competitors and set your brand apart through unique pricing structures, customer experiences, or innovative fulfillment methods. This helps position your brand more efficiently to attract customers and build long-term brand equity.
4. Scalability & Adaptability: A strong business model is designed not just for current success, but for future growth. It enables businesses to expand into new markets while retaining operational control or brand coherence. Moreover, it makes it easier to pivot in response to shifting market dynamics, customer behavior, or emerging technologies.
5. Risk Mitigation: By defining how an eCommerce platform functions and thrives, a solid business model helps reduce operational and financial risks. You can anticipate challenges and navigate uncertainty more effectively with a clear model. Additionally, it allows for better forecasting and resource planning, ensuring greater stability during times of uncertainty.
The Core eCommerce Business Models
A clearly defined eCommerce marketplace model forms the backbone of your eCommerce marketplace. It informs everything from your pricing structure and marketing strategy to customer journey and long-term growth potential. Here, we explore the most prominent eCommerce business models driving the global eCommerce landscape:
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Marketplace Model:
The B2C eCommerce marketplace model is the most widely recognized form of eCommerce that centers around businesses selling products or services directly to individual customers through a digital platform. In this model, the marketplace serves as an intermediary that connects multiple sellers with end-users, offering a broad range of products or services in one place.
Customers browse, compare, and purchase products for personal use, benefitting from competitive pricing, convenience, and a streamlined shopping experience. In a B2C eCommerce marketplace, the entire customer journey is optimized for speed, convenience, and emotional connection. The focus is typically on mass appeal, quick conversions, and delivering a seamless buying experience across devices and platforms.
B2C purchases are largely influenced by need, impulse, social influence, and brand affinity. Hence, to succeed in this space, businesses must master consumer psychology and heavily invest in branding, user experience, and digital marketing.
Example:
- Amazon: Considered as the world’s largest B2C ecommerce marketplace, Amazon offers a wide range of products across diverse categories. It connects third-party sellers and brands with consumers globally, backed by robust logistics, fast delivery, and customer-centric services. Additionally, it also offers services such as Prime, which includes benefits like free and expedited shipping, exclusive deals, access to streaming services, and more.
- ASOS: ASOS is a fashion-focused B2C eCommerce marketplace offering trendy clothing, accessories, and beauty products. It targets young customers with trendy, affordable options, combining its in-house brands with third-party sellers on a global scale.
- Wayfair: Wayfair is a B2C eCommerce marketplace that specializes in home goods, decor, and furniture. It connects consumers with a wide range of suppliers and manufacturers, offering millions of products for every room and style. Known for its competitive pricing, extensive catalog, and user-friendly interface, Wayfair provides detailed product descriptions, customer reviews, and virtual room planning tools to enhance the shopping experience.
Pros:
- Access to a global customer base with diverse needs and preferences.
- Benefit from shorter sales cycles driven by impulse and personal needs.
- Shape your brand identity and messaging without relying on intermediaries.
- Leverage rich customer data from every interaction to personalize marketing.
- Reduced overhead costs by eliminating the need for physical storefronts.
Cons:
- Highly competitive markets demand constant innovation & differentiation.
- Retaining price-sensitive customers requires ongoing marketing efforts.
- Handling logistics, returns, & support at scale adds significant operational pressure.
- Lower average order values and tighter margins reduce profit margins.
- Customer loyalty is short-lived due to shifting preferences & abundant alternatives.
Strategies to Thrive in the B2C eCommerce:
- Stand out with unique branding, exclusive products, or niche positioning.
- Choose a reliable technology partner to build a thriving B2C marketplace.
- Build an emotional connection through compelling brand storytelling.
- Ensure fast, mobile-friendly shopping experiences with frictionless checkout.
- Streamline logistics with reliable fulfillment partners and automated processes.
- Provide responsive, multi-channel customer support with quick resolutions.
- Upsell and bundle products to increase the average order value and margins.
- Continuously test and adapt marketing strategies to align with evolving trends.
2. Business-to-Business (B2B) Marketplace Model:
The B2B eCommerce marketplace model focuses on the digital exchange of goods or services between two commercial entities. These may include manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, or retailers who sell to other businesses rather than directly to end consumers. In this model, the marketplace acts as a centralized hub where multiple businesses connect with other businesses, often facilitating transactions in bulk quantities with customized pricing structures.
The B2B model has undergone a significant transformation over the past decade. What was once dominated by offline catalogs, fax orders, and lengthy negotiations is now increasingly digital-first, powered by custom portals, API integrations, real-time pricing, and automated purchasing workflows. A B2B eCommerce marketplace prioritizes transparency, compliance, and robust functionality, supporting complex workflows such as bulk ordering, tiered pricing, and invoicing. Hence, B2B purchases are driven by logic, long-term value, business requirements, and ROI considerations.
Example:
1. Alibaba: Alibaba is the world’s largest B2B eCommerce marketplace that connects millions of suppliers and buyers globally. It offers a wide range of products across diverse industries, from fashion and beauty to entertainment and construction. The platform supports bulk ordering, customized manufacturing, and cross-border trade.
2. Global Sources: Based in Hong Kong, Global Sources is a trusted B2B eCommerce platform that connects verified suppliers with buyers across the globe. It focuses on electronics, fashion, and home products, offering services such as trade shows, supplier vetting, and industry insights. The platform fosters trusted relationships through quality assurance and curated sourcing tools, and is known for its emphasis on supplier credibility and professional buyer-supplier matchmaking.
3. eWorldTrade: eWorldTrade is a US-based modern B2B eCommerce marketplace that emphasizes digital trade facilitation through verified company listings, secure communication, and advanced lead generation tools. The platform supports industries ranging from agriculture to electronics and offers verified company profiles, digital marketing services, and RFQ tools. Additionally, it focuses on helping small to mid-sized businesses in international trade with ease, cost-effectively and transparently.
Pros:
- Access to a global network of suppliers and buyers.
- Streamlined procurement processes with digital catalogs & automated workflows.
- Enables bulk ordering and volume discounts, benefitting both buyers & sellers.
- Offers personalized pricing, negotiated deals, and credit terms.
- Supports scalability with minimal infrastructure investment.
Cons:
- Longer sales cycle due to complex decision-making processes.
- Requires advanced features like custom catalogs, payment terms, and more.
- High competition can lead to price pressure and reduced margins.
- Trust barriers can increase when dealing with new or overseas suppliers.
- Integration with legacy systems can be time-consuming and costly.
Strategies to Thrive in the B2B eCommerce:
- Showcase verified credentials, transparent pricing, and genuine reviews to build trust.
- Provide advanced platform capabilities like custom catalogs, flexible payment terms, and bulk ordering.
- Leverage turnkey B2B marketplace software for rapid marketplace deployment.
- Offer multiple payment methods, flexible credit terms, and installment options.
- Differentiate beyond price through superior service, product quality, and value-added services.
- Maintain consistent communication and support to foster long-term relationships.
- Ensure mobile optimization and localized content for global accessibility.
- Invest in integration tools or APIs to streamline connections with legacy systems.
Launch a Scalable eCommerce Marketplace Like Alibaba or Global Sources
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) Marketplace Model:
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) eCommerce refers to the facilitation of transactions between individual customers, typically via a third-party digital marketplace that operates as an intermediary. These platforms, also known as Peer-to-Peer (P2P) marketplaces, enable users to list products, communicate with potential buyers, manage transactions, and sometimes handle fulfillment.
In contrast to traditional retail models, C2C marketplace models are decentralized and user-driven. They focus on building scalable infrastructure, consumer trust, and community engagement mechanisms to create liquidity in both supply and demand. This model is central to the resale economy, peer-to-peer services, and circular commerce for secondhand or refurbished goods.
Example:
1. Etsy: Etsy is a niche C2C marketplace that specializes in handmade, vintage, and unique goods. It connects independent artisans and small businesses selling directly to consumers who seek personalized, creative, or custom-made items in categories like crafts, jewelry, and home decor.
2. eBay: eBay is a global C2C eCommerce marketplace that allows individuals to buy and sell new or used goods through auctions or fixed-price listings. Known for its wide product range and secure payment systems, eBay enables smooth peer-to-peer transactions across categories like electronics, collectibles, fashion, and home goods.
3. Depop: Founded in 2011, Depop is a fast-growing C2C eCommerce platform focused on secondhand and vintage fashion, particularly popular among GenZ. It blends social media features with eCommerce and allows users to follow others, like items, and communicate directly. Sellers often showcase their personal style, creating a community-driven marketplace that promotes sustainability, individuality, and circular fashion through peer-to-peer clothing resale.
Pros:
- Low entry barriers allow anyone to become a seller with minimal setup.
- Promotes reuse and sustainability through secondhand product sales.
- Scales organically as more users join and trade on the platform.
- Enables personalized, niche, or vintage item discovery.
- Fosters community through direct individual interactions.
Cons:
- Inconsistent product quality and descriptions may affect buyer trust.
- Limited seller accountability often leads to fraud or disputes.
- User experience can vary greatly depending on individual sellers.
- Slower shipping times due to individual handling & lack of logistics support.
- Lack of standardized return & refund policies.
Strategies to Thrive in the C2C eCommerce:
- Implement strict product listing guidelines with mandatory photos & detailed descriptions.
- Introduce seller verification & rating systems to improve accountability.
- Provide integrated logistics options or shipping partnerships for faster delivery.
- Establish clear, platform-wide return and refund policies to build buyer & seller confidence.
- Incentivize repeat transactions through loyalty programs and promotional tools.
- Utilize AI and data analytics to personalize product discovery for buyers.
- Foster an active community with engaging features like chat, likes, and follows.
4. Business-to-Government (B2G) Marketplace Model:
Business-to-Government (B2G) eCommerce, also referred to as Business-to-Administration (B2A), is the commercial eCommerce business model in which private enterprises sell products or services to government agencies at various levels, be it local, state, national, or international.
Transactions in such models are typically regulated through formal procurement processes, public tenders, bid solicitations, and government-approved vendor contracts. Unlike other eCommerce business models, B2G models involve a stringent framework of compliance, transparency, documentation, and service-level agreements.
B2G models often include high-stakes industries such as public health, national defense, transportation infrastructure, IT modernization, disaster recovery, and education.
Example:
1. Amazon Business (GSA-approved): Amazon Business is a GSA-approved eCommerce platform that enables government agencies to purchase office supplies, IT hardware, and industrial goods. It offers federal compliance, tax-exempt purchasing, and bulk ordering, streamlining procurement processes for public sector organizations.
2. United States Federal Marketplace (FMP): The Federal Marketplace is a US government initiative that consolidates acquisition programs and procurement tools. It simplifies how federal agencies connect with qualified vendors for goods and services through a digital portal aligned with modern eCommerce practices.
3. Cisco & Microsoft: Cisco & Microsoft engage in B2G eCommerce by serving as major providers, offering secure cloud infrastructure, cybersecurity solutions, and enterprise software tailored to government needs.
Pros:
- Offers stable, large-scale contracts with guaranteed government payments.
- Enhances credibility and reputation for businesses working with government bodies.
- Provides long-term business opportunities through repeat procurement cycles.
- Reduces market risks through reliable demand from public sector agencies.
- Encourages compliance-driven operations and process improvements.
Cons:
- Lengthy & complex bidding and approval processes can delay deals.
- High regulatory and compliance requirements increase the administrative burden.
- Intense competition among vendors for limited government contracts.
- Limited pricing flexibility due to fixed budget allocations and bidding rules.
- Payments may be delayed due to bureaucratic processing timelines.
Strategies to Thrive in the B2G eCommerce:
- Understand & comply with all government procurement regulations & documentation requirements.
- Invest in certifications, security clearances, and compliance audits to qualify for tenders.
- Integrate advanced features and build a tailored B2G eCommerce platform to reflect a unique brand identity.
- Focus on niche capabilities or specialized solutions to reduce competition in broad contract categories.
- Invest in cybersecurity and data protection to meet stringent government standards.
5. Consumer-to-Business (C2B) Marketplace Model:
Consumer-to-Business (C2B) eCommerce is a reverse eCommerce marketplace model in which individual consumers create value that is consumed or monetized by businesses, effectively inverting the traditional commercial value chain.
In this paradigm, the marketplace acts as a facilitator that connects consumers, such as freelancers, influencers, content creators, or data providers, with businesses seeking their skills. Unlike B2C, where businesses initiate product delivery to end-users, the C2B model empowers consumers as active participants in the value chain.
This model has flourished in the digital era with the rise of the gig economy, freelance marketplaces, user-generated content, influencer marketing, and data-as-a-service ecosystems. C2B transactions are driven by personalization, reputation, niche expertise, and the ability to scale on demand.
Hence, success in the C2B space hinges on creating a dynamic, secure, and flexible environment where consumers feel valued and businesses can tap into unique, often untapped, market resources.
Example:
1. Freelance Platforms: Freelance marketplaces like Upwork or Fiverr allow individuals to offer professional services, such as writing, design, and programming, to businesses seeking on-demand talent. These platforms facilitate project-based work, enabling consumers to monetize their expertise while providing businesses with flexible and scalable solutions that avoid long-term hiring commitments.
2. Stock Media & Digital Asset Platforms: Platforms like Shutterstock or Envato enable consumers to upload and sell digital assets such as photos, videos, music, and templates. Businesses can purchase these assets for marketing, design, or content needs, offering creators with recurring revenue while providing companies with high-quality, affordable media resources.
3. Affiliate & Referral Models: Affiliate networks such as Amazon Associates or ShareASale allow individuals to promote products and earn commissions on generated sales. While businesses benefit from increased exposure and customer acquisition, affiliates monetize their content, audience reach, or influence through targeted promotions.
4. Consumer Research & Feedback Platforms: Websites like G2, UserTesting, or Respondent pay individuals to provide feedback, opinions, or usability testing for business products or services. Businesses use this input for market research and product development, turning consumers into valuable resources of insights and innovation.
Pros:
- Access to diverse, specialized content on demand.
- Cost-effective compared to hiring full-time employees.
- Encourages innovation through consumer-driven input.
- Empowers individuals to monetize their skills.
- Scalable for short-term or project-based needs.
Cons:
- Quality and consistency of consumer services may vary.
- Trust and credibility can be hard to establish initially.
- High competition may drive down consumer earnings.
- Regulatory and compliance issues across borders.
- Payment disputes or delays may arise.
Strategies to Thrive in the C2B eCommerce:
- Create a secure, user-friendly C2B platform that makes onboarding & transactions simple.
- Set clear quality standards and provide training resources to maintain consistency.
- Provide tools for portfolio building, reviews, and skill showcasing to attract customers.
- Implement robust vetting systems to ensure the quality & credibility of service providers.
- Encourage niche specialization to attract a loyal customer base.
- Foster community engagement through forums and resource sharing.
- Introduce flexible pricing models to accommodate diverse business budgets & project scopes.
- Implement secure, transparent payment systems with escrow and dispute resolution tools.
6. Business-to-Business-to-Consumer (B2B2C) Marketplace Model:
The Business-to-Business-to-Consumer (B2B2C) model is a hybrid strategy that blends the best aspects of B2B and B2C commerce. In this structure, one business (manufacturer, service provider, or brand owner) supplies goods or services to another business (such as a distributor, marketplace, or retailer), which then delivers those offerings to end consumers.
What differentiates the B2B2C marketplace model from traditional B2B distribution is the shared ownership of the customer experience. Brands in this model often retain visibility, influence, or even direct communication with the end consumer. Additionally, it often involves co-branded platforms, integrated APIs, or white-label partnerships, where the end consumer interacts with a brand interface that may mask the complexity of business partnerships behind it.
Example:
1. Instacart: Instacart operates a B2B2C model by partnering with grocery retailers to deliver products to consumers via its platform. It provides retailers with digital infrastructure and logistics, while consumers benefit from convenient online grocery shopping and home delivery.
2. Amazon FBA (Fulfilled by Amazon): Amazon FBA enables third-party sellers to list products on Amazon (B2B), while Amazon handles warehousing, packing, and shipping to consumers (B2C). This B2B2C model allows sellers to scale quickly and deliver a seamless customer experience through Amazon’s trusted infrastructure and vast customer base.
3. Fintech-as-a-Service: Platforms like Stripe or Square offer embedded financial services (such as payments, lending, or banking) to businesses, which then provide these services to their customers. This B2B2C model powers seamless payment experiences, financing, or banking services within third-party apps, creating a smooth transaction layer between businesses and end consumers.
Pros:
- Expands consumer reach by combining businesses and consumers.
- Enables rapid scaling through partner networks.
- Strengthens brand credibility through trusted platforms.
- Encourages innovation through collaborative ecosystems.
- Generates multiple revenue streams for both B2B and B2C ends.
Cons:
- Complex coordination between multiple stakeholders.
- Risk of brand dilution due to shared customer ownership.
- High operational and integration costs.
- Challenges in maintaining a consistent user experience.
- Dependency on partner performance and reliability.
Strategies to Thrive in the B2B2C eCommerce:
- Implement strong project management frameworks to streamline coordination between stakeholders.
- Use co-branding guidelines and marketing oversight to prevent brand dilution.
- Adopt scalable, cost-efficient eCommerce marketplace solutions to reduce operational expenses.
- Implement shared data analytics to optimize performance across the value chain.
- Establish shared customer experience standards to ensure consistency.
7. Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Marketplace Model:
The Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) eCommerce is a retail strategy where manufacturers or brands sell their own products or services to end consumers, bypassing all intermediaries such as wholesalers, distributors, and third-party retailers.
D2C eCommerce is typically executed through digital channels, such as proprietary websites, mobile apps, and social commerce platforms, where businesses have complete control over branding, pricing, marketing, and customer experience. Unlike conventional retail models, D2C brands own the entire customer journey, from awareness and consideration to purchase and post-sale service. It gives brands the autonomy to innovate quickly, personalize experiences at scale, and build loyal communities around their offerings, all without the friction of third-party gatekeeping.
D2C eCommerce marketplace models are especially popular among digitally native vertical brands and are becoming a cornerstone strategy for both startups and legacy brands undergoing digital transformation.
Example:
1. Nike: Nike uses a hybrid D2C model, selling directly to consumers through its branded stores, website, and app. It focuses on personalized customer experiences, loyalty programs, and exclusive products, reducing reliance on third-party retailers while enhancing brand control and customer data insights.
2. Casper: Casper operates as a digitally native vertical brand, selling mattresses and sleep products directly through its website and selected branded retail stores. By cutting out intermediaries, its D2C model reduces costs, emphasizes convenience, and streamlines the supply chain to offer high-quality products at competitive prices.
3. Tesla: Tesla bypasses traditional dealerships with its D2C model, selling vehicles directly to consumers via its website and company-owned showrooms. This approach provides better control over pricing, user experience, transparency, and customer relationships.
Pros:
- Complete control over branding and customer experience.
- Higher profit margins by cutting out intermediaries.
- Faster feedback loops for product improvement.
- Enhanced customer loyalty through direct relationships.
- Greater pricing control and flexibility.
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost for infrastructure and marketing.
- Managing logistics and fulfillment can be complex.
- Dependence on digital channels increases competition.
- Challenging to scale rapidly without established networks.
- Requires significant investments in preventing cybersecurity threats.
Strategies to Thrive in the D2C eCommerce:
- Start lean with scalable & customizable eCommerce platforms to reduce upfront infrastructure costs.
- Build a strong brand identity that resonates emotionally with your target audience.
- Invest in a high-quality digital storefront optimized for mobile and SEO.
- Differentiate through unique value propositions to stand out.
- Continuously gather and act on customer feedback for product innovation.
- Ensure robust cybersecurity measures to protect customer data and trust.
- Use social commerce and influencer partnerships to drive traffic and awareness.
Launch a High-Performing eCommerce Marketplace that Grows Exponentially
8. Hybrid Marketplace Model:
A hybrid eCommerce business model refers to a multifaceted strategy that combines two or more eCommerce marketplace models into a single integrated strategy. Hybrid models allow businesses to operate across multiple customer segments, sales channels, or fulfillment methods, often blending various marketplace models into one.
At its core, the hybrid model reflects the omnichannel reality of modern commerce, where consumers and business buyers interact with brands across numerous touchpoints. Rather than choosing a single path, businesses orchestrate a cohesive commerce ecosystem that allows them to serve different segments in different ways. This model is often favored by mid-sized to enterprise-level organizations, as well as fast-scaling eCommerce setups, because it enables them to diversify risk, test new revenue streams, and respond dynamically to shifting consumer behaviors and supply chain disruptions.
While operationally complex, the hybrid model is built on the premise of commerce convergence, bringing together multiple models into a unified business model that enhances brand resilience, profitability, and customer reach.
Core Hybrid Approaches:
- Brand-Owned D2C + Third-Party Retailers: Brands sell on Amazon, Walmart, Etsy, etc., for maximum reach, but maintain their own branded site for loyalty and storytelling.
- Retail + eCommerce: Combines online D2C sales with physical retail stores to offer a seamless omnichannel experience.
- Branded Marketplace Model: Brands sell their own products and also host third-party sellers on their platforms to expand product offerings and diversify revenue channels.
- Wholesale + D2C Channels: Brands operate D2C storefronts while also distributing through wholesale B2B retail partners for broader reach.
Example:
1. Samsung: Samsung operates its own D2C eCommerce platform while also selling through major retailers like Amazon, Best Buy, and more. It combines direct sales, third-party distributions, and B2B partnerships to maximize reach and maintain control over the customer experience and product positioning.
2. Nestle: Nestle blends D2C and B2B models by offering selected products via its own eCommerce platforms (e.g., Nespresso). It also partners with platforms like Amazon for subscription offerings, while selectively hosting branded experiences and product bundles, merging convenience with customer retention across multiple channels.
3. Adobe: Adobe utilizes a hybrid marketplace by selling software directly via its website while also partnering with resellers, B2B platforms, and cloud partners like AWS. Additionally, its Adobe Exchange marketplace hosts third-party plugins and extensions, creating an ecosystem that supports both internal offerings and external developers. This hybrid model supports both individual creators and enterprise clients, combining D2C digital delivery with global B2B distribution.
Pros:
- Expands customer reach across multiple channels.
- Diversifies revenue streams for greater financial resilience.
- Enables upselling through curated third-party offerings.
- Enhances customer convenience via omnichannel presence.
- Leverages data from multiple touchpoints for better insights.
Cons:
- Increases operational complexity across channels.
- Requires competitive pricing and careful inventory coordination
- Higher risk of channel conflicts and cannibalization
- Demands more advanced logistics and fulfillment systems.
- May involve complex vendor and partner management.
Strategies to Thrive in the Hybrid eCommerce:
- Define clear channel strategies to avoid conflicts and ensure brand consistency.
- Implement centralized inventory and order management to streamline multi-channel operations.
- Use dynamic pricing strategies to stay competitive while protecting profit margins.
- Establish clear channel governance policies to minimize conflicts.
- Continuously test and refine new combinations of marketplace models for growth.
- Balance automation with human oversight to manage complexity efficiently.
- Create strong vendor and partner management frameworks with clear KPIs and communication protocols.
Smart eCommerce Fulfillment Models Transforming Online Retail
In a competitive eCommerce environment, how you deliver value is just as critical as what you sell. Modern businesses are no longer bound to traditional retail models; advances in technology, supply chain optimization, and customer behavior shifts have given rise to a variety of value delivery approaches. Below are the key value delivery methods that are shaping today’s eCommerce landscape:
1. White Label:
White labeling enables a business to rebrand and sell products manufactured by some other company under its own brand identity. This approach allows for rapid market entry without the high upfront investment in R&D or manufacturing. Businesses focus on branding, marketing, and distribution while leveraging third-party manufacturing capabilities.
– Ideal for: Businesses looking to leverage established products or designs without building from scratch.
– Key Benefit: Quick scalability with minimal product development risk.
– Limitation: Limited differentiation until supported by strong branding and customer experience.
2. Private Label:
Private label products are manufactured by a third party but sold exclusively under the retailer’s brand. Unlike white label goods, private-label products are developed with distinct specifications, packaging, and branding, providing a higher degree of differentiation. Retail giants and niche D2C brands alike employ this model to strengthen brand equity and pricing power.
– Ideal for: Brands seeking exclusivity and differentiation in crowded markets.
– Key Benefit: Greater brand ownership and exclusivity.
– Limitation: Higher upfront investment in product design and manufacturing.
3. Wholesale:
Wholesaling remains a cornerstone of B2B eCommerce. It involves purchasing products in bulk directly from manufacturers or distributors and reselling them to retailers or institutional buyers. This model benefits from economies of scale but requires significant capital investment and inventory management capabilities. However, in today’s digital age, wholesale platforms have evolved into fully integrated eCommerce solutions, offering order automation, bulk discounts, and multi-channel inventory visibility.
– Ideal for: Businesses with the infrastructure to handle bulk stock and a strategy to move large volumes efficiently.
– Key Benefit: Achieve economies of scale and maintain a reliable, predictable supply chain.
– Limitation: Requires significant capital investment for bulk purchasing and storage.
4. Dropshipping:
Dropshipping completely eliminates inventory management from the entire eCommerce operation. Sellers market products and process orders, while a third-party supplier handles storage, packaging, and direct delivery to the customer. This low-risk model reduces upfront costs and operational complexities, but often demands careful supplier vetting to maintain quality and service standards.
– Ideal for: Businesses exploring or testing new product categories without heavy capital investment.
– Key Benefit: Minimal capital requirements and operational flexibility.
– Limitation: Lower margins and reduced control over fulfillment speed and quality.
5. Subscription Services:
Subscription commerce focuses on recurring revenue, weekly, monthly, or annually, by delivering products or services at regular intervals. This method fosters customer loyalty and provides a predictable cash flow. Whether it’s consumables, curated boxes, or premium digital content, this subscription model thrives when coupled with personalization and customer engagement strategies.
– Ideal for: Products or services with repeat purchase potential.
– Key Benefit: Recurring, predictable revenue and stronger lifetime customer loyalty.
– Limitation: Requires consistent value delivery to avoid churn.
6. Print on Demand (POD):
Print on Demand allows businesses to sell custom-designed products, such as apparel, accessories, home decor, or stationery, without holding inventory. Items are produced and shipped only when a customer places an order, enabling virtually unlimited product variations without upfront manufacturing costs. This model combines creative flexibility with low operational risks, thriving on design agility and trend responsiveness.
– Ideal for: Businesses that thrive on personalization, creative designs, or trend-driven products.
– Key Benefit: Zero inventory risk and rapid product experimentation
– Limitation: Longer fulfillment times and potentially lower margins.
How to Choose the Right eCommerce Business Model?
Selecting the right business model to build an eCommerce marketplace is a strategic decision that shapes the platform’s market positioning, operational structure, revenue potential, and ability to scale. The right choice is rarely about following trends, but aligning the model with your core value proposition, target audience, and business capabilities.
Here are the key considerations to make an informed decision:
1. Define Your Target Market and Audience: A precise understanding of your target audience is essential to determine the right eCommerce business model for your marketplace. Determine whether your primary focus is B2B, B2C, B2G, B2B2C, or a strategic blend. Take the following factors into account:
- Purchase Decision Cycle: B2B transactions typically involve longer decision-making cycles due to multiple stakeholders and consultative processes. In contrast, B2C decisions are often faster and driven by emotions, impulse, or seasonal trends. Hence, understand which cycle suits your business vision and its ability to cater to it.
- Price Sensitivity: High-value, complex solutions generally call for a B2B model, which allows for tailored pricing and long-term relations, while B2C markets might be more price-sensitive, requiring a model that offers competitive pricing or bulk purchases.
- Order Volume and Frequency: B2B transactions often involve high-volume, recurring transactions. Whereas, B2C purchases tend to be smaller and more specific.
2. Evaluate Your Value Proposition: The chosen eCommerce business model determines the strengths of your eCommerce marketplace. Consider whether you deliver bespoke solutions, brand-led experiences, or price-driven value. Additionally, select a definite structure that best communicates and monetizes. The goal is to ensure that the business model amplifies your value proposition.
3. Assess Operational Capabilities: The operational readiness determines the feasibility of the platform. Evaluate the ability to manage inventory, maintain stock levels, fulfillment speed, and technology integration. The operational infrastructure must support your chosen eCommerce business model efficiently, ensuring reliability, scalability, and compliance with service-level commitments across all touchpoints.
4. Consider Revenue Predictability: Revenue predictability plays a significant role in shaping your eCommerce business model. Certain models, such as subscription services, that offer recurring revenue can be more valuable over time. In contrast, others rely on transactional volume, where income fluctuates depending on the demand and activity. Understanding these differences thus helps you align financial planning with business stability.
5. Analyse Market Competition and Differentiation: Evaluate market saturation, competitor positioning, and pricing strategies to position your eCommerce marketplace effectively. In highly competitive segments, niche targeting, product customization, or fulfillment speed can become key differentiators. Establishing a competitive differentiation strategy ensures long-term visibility and brand value.
6. Factor in Scalability & Adaptability: Choose a business model that scales efficiently into global markets without compromising performance and creating complexity. Ensure operational processes, technology, and supplier relationships can handle increased demand. Additionally, choose a structure that can adapt in response to the changes without requiring a complete overhaul.
7. Test and Validate Before Deployment: Conduct thorough testing through MVP launches and limited product releases before committing substantial resources and complete deployment. These initiatives verify demand, refine operational workflows, and identify unforeseen challenges, increasing the likelihood of a smooth, profitable scale-up.
Ready to Build a Marketplace that Stands Out in the Competition?
Which eCommerce Business Model is Popular in 2025?
Multi-vendor marketplace models emerge as a dominant force in the eCommerce industry today. According to an analysis, marketplaces now account for 67% of global online sales, outpacing traditional commerce.
Within this trend, B2C and hybrid eCommerce business models remain highly competitive, with D2C strategies gaining particular traction for their ability to provide complete control over branding & customer journey, maximize margins, and deliver personalized experiences. Additionally, B2B marketplaces are surging too. A report by Gartner suggests that 80% of B2B buyers will shift to digital marketplaces over legacy platforms.
Alongside these, subscription-based models continue to gain momentum by generating predictable recurring revenue and fostering strong customer loyalty. AI-powered personalization, omnichannel presence, voice commerce, and mobile-first experiences enable brands to deliver a consistent, personalized experience.
Furthermore, Quick Commerce is also gaining massive popularity, offering ultra-fast deliveries that meet rising consumer demands for convenience, especially in urban areas.
Best eCommerce Marketplace Software to Build a Thriving Marketplace
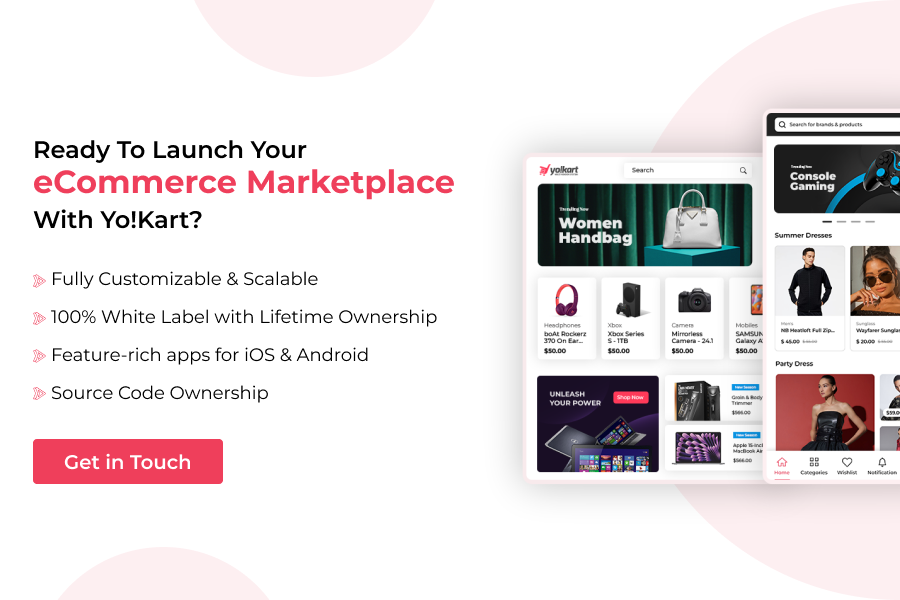
When it comes to building a robust, scalable eCommerce marketplace, Yo!Kart stands out as the most reliable eCommerce marketplace software available in the market. It is a turnkey, ready-to-launch marketplace software that allows businesses to launch their own digital marketplace across diverse niches. Designed specifically for multi-vendor operations, Yo!Kart can be customized to build an eCommerce marketplace that supports multiple business models, including B2C, B2B, and more.
Here are the key benefits businesses gain by choosing Yo!Kart:
- 100% white label solution that allows you to design the platform to your unique branding.
- Highly customizable software, allowing you to adapt to diverse eCommerce business models.
- Self-hosted solution provides you the flexibility to host the software on your preferred choice of server.
- Lifetime ownership with a one-time investment and no monthly or annual recurring charges.
- Highly affordable software with base white label pricing packages starting from $999.
- Extensively scalable solution with multilingual & multi-currency support to expand to global markets.
- With over a decade of industry experience, Yo!Kart is trusted by businesses worldwide and has powered more than 5,000 unique marketplaces.
- Free demo availability to explore the functionalities of the software firsthand.
- Native mobile apps available for both Android and iOS platforms for a go-to buyer experience.
- 1 year of free technical support post purchase to help in case of any unforeseen bugs or downtimes.
Additionally, Yo!Kart not only provides core eCommerce functionalities but also focuses on customer experience, vendor management, and performance analytics, making it easier for marketplace owners to attract sellers & retain buyers to maximize revenue. Whether yo’re starting a niche marketplace or aiming for a global audience, Yo!Kart offers the flexibility, speed, and reliability to thrive in today’s competitive eCommerce landscape.
Secure a Personalized Demo Session to Explore the Functionalities of Yo!Kart
Conclusion
In an ever-evolving digital landscape, the eCommerce marketplaces have emerged as a crucial force propelling industry growth. Selecting the right eCommerce business model is a strategic decision that directly shapes customer experience, operational efficiency, and long-term profitability. Each eCommerce business model offers distinct opportunities and considerations. The key is to align the chosen model with the business’s core strengths, target audience, and long-term objectives, while remaining agile enough to evolve. The right model not only optimizes revenue streams but also creates a sustainable competitive advantage.
FAQs
Q 1. How do I know which eCommerce business model is right for me?
Ans. Choosing the right eCommerce business model depends on factors like target audience, product types, budget, and long-term goals. Start by analyzing the product or service you’re selling, how much control you want over your inventory, and whether you want to deal with logistics or not. Doing market research and understanding your niche will help you know the right eCommerce business model for your marketplace.
Q 2. How does eCommerce business model innovation affect customer experience?
Ans. Innovation in eCommerce business models can significantly enhance customer experience by offering more personalized, seamless, and convenient shopping. Adopting a subscription, marketplace, or on-demand model, for instance, can enhance the customer experience by offering personalized, flexible, and convenient shopping options. Such models often provide unique value propositions that provide customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Q 3. Can I combine multiple eCommerce business models while building a marketplace?
Ans. Yes, it is possible to integrate multiple eCommerce business models within a single marketplace. Hybrid models allow for greater flexibility, catering to a broader customer base and expanding your offerings while providing diverse revenue streams.
Q 4. What are the risks of choosing the wrong eCommerce business model to build an eCommerce marketplace?
Ans. Choosing the wrong eCommerce business model can lead to inefficiencies, loss of market relevance, and financial strain. For example, a B2C model in a market that favors C2C may not attract the right audience. Risks also include scaling issues, inadequate customer experience, and difficulties in managing operations or inventory. Hence, proper market research and a solid business plan are essential to avoid any risks of failure.
Q 5. Does a readymade marketplace software allow to build an eCommerce marketplace that caters to multiple eCommerce business models?
Ans. Yes, many readymade marketplace software like Yo!Kart are designed to support multiple eCommerce business models to build a marketplace. Such software provides flexibility to build and scale your marketplace effortlessly, allowing you to adapt to various business needs and user types.
Q 6. Which is the best eCommerce marketplace software to build a marketplace?
Ans. Among many solutions available in the industry, Yo!Kart stands out to be the ultimate eCommerce marketplace software that allows you to build an eCommerce marketplace across multiple business models, whether B2B, B2C, or more. Its rich set of features, robust clientele, industry experience, integrated payment gateways, customizable themes, and extensive scalability options make it an excellent choice for entrepreneurs looking to build an eCommerce marketplace.