Published Date 22 Jan, 2026
The digital economy has evolved rapidly over the last decade. Instead of building standalone online stores, entrepreneurs and enterprises are increasingly investing in multi-seller marketplace platforms, business models designed to connect buyers and sellers at scale. From global giants like Amazon and Etsy to niche-focused platforms serving services, rentals, or B2B trade, marketplaces are now one of the most powerful and scalable online business models.
Thus, if you are an entrepreneur planning to build a multi-seller marketplace, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from understanding marketplace fundamentals and choosing the right business model to selecting the best development approach and launching with the right technology.
Table of Contents
- What is a Multi-Seller Marketplace?
- Popular Types of Multi-Seller Marketplaces
- Benefits of Building a Multi-Seller Marketplace
- Key Features Required in a Multi-Seller Marketplace
- Choosing the Right Business Model
- Key Steps to Build a Multi-Seller Marketplace
- Marketplace Development Approaches: Build vs Buy
- How to Choose the Right Approach for Your Marketplace
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Multi-Seller Marketplace?
A multi-seller marketplace is an online platform where multiple independent sellers list and sell their products or services and serve customers through a single, centralized website or app. The marketplace owner operates and manages the platform, including traffic generation, payments, and overall user experience, while sellers focus on managing listings and fulfilling orders.
This model enables businesses to scale faster by bringing buyers and sellers together under one unified ecosystem.
How It Works
- Buyers browse and purchase products or services from multiple sellers on one platform
- Sellers register on the marketplace, list their offerings, and manage orders independently
- Marketplace admin controls commissions, seller policies, payouts, and platform operations
Single-Vendor vs Multi-Seller Marketplace
| Aspect | Single-Vendor Store | Multi-Seller Marketplace |
| Inventory | Owned by a business | Owned by sellers |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Revenue | Product margins | Commissions, fees, and others |
| Risk | High inventory risk | Distributed risk |
This distributed model is what makes marketplaces more resilient and scalable than traditional eCommerce stores.
Popular Types of Multi-Seller Marketplaces
Multi-seller marketplaces can be structured in several ways depending on what is being sold, who the buyers are, and how transactions are being made. Understanding these marketplace types early helps entrepreneurs choose the right business model, feature set, and technology foundation from the start, reducing risk and improving long-term scalability.
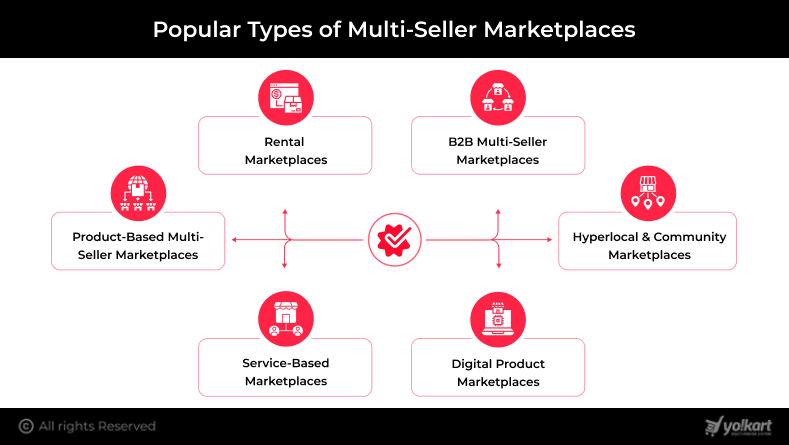
1. Product-Based Multi-Seller Marketplaces
Product-based marketplaces allow multiple vendors to sell physical or digital goods through a single platform. While the marketplace manages product discovery, payments, and often logistics coordination, sellers handle inventory and order fulfillment.
Key Characteristics
- Large and diverse product catalogs
- Commission-based revenue model
- Inventory and pricing are managed by sellers
- Strong emphasis on search, filters, and customer reviews
Common Use Cases
- General eCommerce marketplaces
- Niche product platforms, such as handmade goods, electronics, fashion, and groceries
- Local or regional seller aggregation platforms
Examples: Amazon, Flipkart, Etsy
2. Service-Based Marketplaces
Service marketplaces connect individuals or businesses offering services with customers looking for professional or on-demand services. These platforms focus heavily on scheduling, availability, communication, and trust signals.
Key Characteristics
- Detailed seller profiles and service packages
- Time-based or project-based pricing
- Booking, scheduling, and cancellation workflows
- Ratings, reviews, and identity verification
Common Use Cases
- Freelance and professional services
- Home services and local professionals
- Consulting, coaching, and education platforms
Examples: Fiverr, Upwork, Urban Company
3. Rental Marketplaces
Rental marketplaces enable sellers to list assets that can be rented for a specific duration, rather than sold permanently. These platforms require advanced booking management, availability tracking, and trust-building features.
Key Characteristics
- Time-based availability calendars
- Security deposits and damage protection policies
- Booking confirmation and cancellation workflows
- Trust and verification mechanisms
Common Use Cases
- Vacation rentals and accommodations
- Vehicle, tool, or equipment rentals
- Fashion and luxury item rentals
Examples: Airbnb, equipment rental platforms
4. Digital Product Marketplaces
Digital product marketplaces specialize in non-physical goods that can be delivered instantly after purchase. These platforms prioritize secure access control and intellectual property protection.
Key Characteristics
- Instant downloads or gated access to content
- License and usage management
- Digital rights protection
- No logistics or shipping dependencies
Common Use Cases
- Online courses and learning platforms
- Software, themes, plugins, templates
- Music, eBooks, and digital artwork
Examples: Udemy, ThemeForest
5. B2B Multi-Seller Marketplaces
B2B marketplaces facilitate trade and transactions between businesses, manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, and retailers. These platforms focus on efficiency, bulk pricing, negotiations, and long-term business relationships.
Key Characteristics
- Bulk ordering and MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) management
- Custom pricing and quotation systems
- RFQs (Request for Quotation)
- Role-based access and approvals
Common Use Cases
- Wholesale trade platforms
- Manufacturing and sourcing portals
- Industry-specific procurement marketplaces
Examples: Alibaba-style platforms, niche industry portals
Suggested Read: Top B2B eCommerce Platforms in 2026
6. Hyperlocal & Community Marketplaces
Hyperlocal marketplaces focus on a specific geographic area, connecting nearby buyers and sellers. It also enables faster fulfillment and localized services.
Key Characteristics
- Location-based search and listings
- Same-day or short-distance fulfillment
- Simplified local seller onboarding
- Community-driven trust models
Common Use Cases
- Local grocery and food delivery
- Neighborhood service providers
- City-specific classifieds and rentals
Examples: Instacart, DoorDash
Build a Marketplace Aligned With Your Niche
Benefits of Building a Multi-Seller Marketplace
Building a multi-seller marketplace offers strategic advantages that extend far beyond traditional eCommerce models. By enabling multiple sellers to operate on a single platform, marketplace owners can unlock scalability, diversification, and long-term growth with significantly lower operational risk. Let’s have a look at some of the benefits of building a multi-seller marketplace:
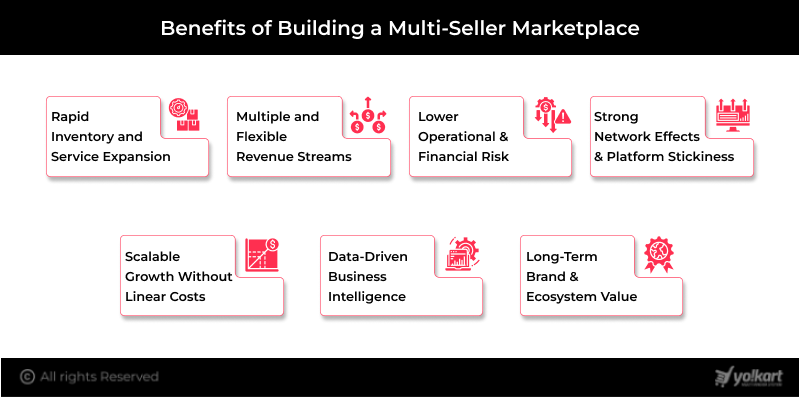
1. Rapid Inventory and Service Expansion
Unlike single-vendor stores, a multi-seller marketplace does not rely on owned inventory. Each new seller brings their own products or services to the platform, allowing the marketplace to grow organically without heavy upfront investment. This enables faster catalog expansion and quicker market entry.
2. Multiple and Flexible Revenue Streams
Multi-seller marketplaces are not limited to a single income source. Depending on the business strategy, revenue can be generated through multiple channels, including:
- Transaction-based commissions
- Seller subscriptions or membership plans
- Listing or onboarding fees
- Featured listings and sponsored placements
This flexibility helps multi-seller marketplaces remain resilient and profitable even during market fluctuations.
3. Lower Operational and Financial Risk
Since sellers manage their own inventory, pricing, and fulfillment, the marketplace owner avoids the risks associated with warehousing, unsold stock, and logistics. The platform functions as an intermediary, significantly reducing capital exposure while maintaining revenue potential.
4. Strong Network Effects and Platform Stickiness
As more sellers join the marketplace, buyers benefit from a wider selection, better pricing, and more options. This increased buyer activity, in turn, attracts more sellers, creating a powerful network effect that drives organic growth and strengthens the platform’s competitive position.
5. Scalable Growth Without Linear Costs
Multi-seller marketplace growth is driven by participants rather than physical resources. Expanding the platform does not require proportional increases in inventory, staff, or infrastructure, making the model highly scalable and cost-efficient in the long run.
6. Data-Driven Business Intelligence
Marketplaces generate valuable data insights into buyer behavior, seller performance, pricing trends, and demand patterns. This data can be leveraged to optimize commissions, improve user experience, and introduce new monetization opportunities.
7. Long-Term Brand and Ecosystem Value
Successful marketplaces evolve into full ecosystems rather than simple sales platforms. Over time, they build trust, brand recognition, and seller dependency, making the business more defensible, attractive to investors, and valuable as a long-term digital asset.
Suggested Read: A Detailed Guide For Multi-Vendor Marketplace Development
Key Features Required in a Multi-Seller Marketplace
The success of a multi-seller marketplace largely depends on how effectively it serves the needs of buyers, sellers, and administrators. A comprehensive suite of marketplace features ensures smooth operations, builds trust among users, and supports long-term scalability. Further, given below are the key features required in a multi-seller marketplace:
1. Seller-Centric Features
Sellers are the backbone of any marketplace, and their experience directly impacts platform growth. Hence, to offer a seamless experience to sellers, your marketplace should include:
- Simple seller registration and verification process
- Intuitive dashboard to manage products or services
- Inventory, pricing, and availability control
- Order management and fulfillment tracking
- Sales reports, earnings summaries, and performance insights
A frictionless seller experience encourages onboarding, retention, and higher-quality listings.
2. Buyer-Centric Features
Buyers expect convenience, transparency, and security while shopping on a marketplace. A smooth buying experience builds confidence and encourages repeat transactions.
- Advanced search, filters, and category navigation
- Detailed product or service pages with seller information
- Secure checkout with multiple payment options
- Order tracking and communication tools
- Ratings, reviews, and trust indicators
These features reduce purchase friction and strengthen buyer loyalty.
3. Admin & Platform Management Features
Marketplace administrators need complete visibility and control to manage operations efficiently. Thus, your marketplace should incorporate:
- Seller approval, suspension, and performance monitoring
- Flexible commission and fee configuration
- Automated payout and settlement management
- Dispute, refund, and return handling
- Analytics dashboard for sales, traffic, and growth insights
Strong admin controls help maintain quality standards, regulatory compliance, and overall profitability.
4. Marketplace Essentials
Beyond core workflows, certain foundational features are critical for long-term sustainability and growth. They include:
- Mobile-responsive design for all devices
- SEO-friendly URLs and page structure
- Scalable architecture to handle growing traffic and transactions
- Secure data handling and payment processing
- Integration readiness for third-party tools and services
These features ensure the marketplace is not only functional at launch but also ready to grow without costly rebuilds.
Want to Turn Your Marketplace Idea Into Reality?
Choosing the Right Business Model
Selecting the right business model is a critical step when building a multi-seller marketplace. It directly impacts revenue predictability, seller adoption, and long-term scalability. However, the right choice depends on your marketplace type, target sellers, transaction volume, and growth stage.
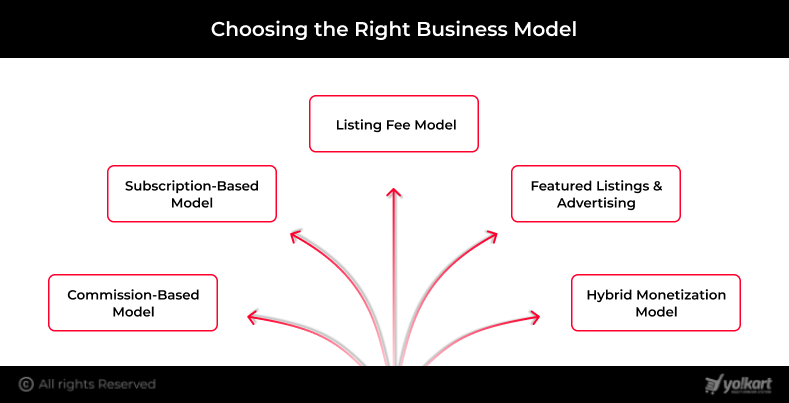
1. Commission-Based Model
In this model, the marketplace earns a percentage from every successful transaction made through the platform. As sellers generate more sales, the marketplace earns more, making this model attractive for high-volume platforms focused on growth and long-term scale.
Why it works
- Low entry barrier for sellers
- Revenue grows as transaction volume increases
- Aligns marketplace success with seller success
Best suited for: Product, service, and rental marketplaces with consistent transaction flow.
2. Subscription-Based Model
Sellers pay a fixed recurring fee, either monthly or annually, to access the marketplace and its features. This model works best when sellers receive ongoing value through leads, tools, or exposure that justifies a recurring commitment.
Why it works
- Predictable and recurring revenue
- Encourages serious and committed sellers
- Simplifies earnings forecasting
Best suited for: B2B platforms, professional service marketplaces, or niche communities with high seller value.
3. Listing Fee Model
Sellers are charged a fee for posting products or services on the platform. It is effective when seller demand is high and listings provide immediate visibility or access to a targeted audience.
Why it works
- Generates upfront revenue
- Helps control low-quality or spam listings
- Easy to implement
Best suited for: Classified-style or niche marketplaces with high seller demand.
4. Featured Listings & Advertising
Sellers pay to increase visibility through promoted listings or ads. As buyer traffic grows, promoted placements become a valuable, high-margin revenue stream.
Why it works
- High-margin revenue stream
- Optional for sellers
- Scales well as competition increases
Best suited for: Mature marketplaces with strong buyer traffic.
5. Hybrid Monetization Model
This approach combines two or more revenue models, such as commissions plus subscriptions or featured listings. It allows marketplaces to adapt pricing strategies over time while reducing dependency on a single revenue stream.
Why it works
- Diversifies income sources
- Reduces dependency on a single revenue stream
- Adapts well as the marketplace scales
Best suited for: Marketplaces planning long-term growth and monetization flexibility.
How to Choose the Best Model for Your Marketplace?
When deciding on a monetization strategy, consider:
- Seller acquisition vs revenue priorities
- Average order value and transaction frequency
- Competitive landscape
- Long-term scalability and flexibility
A well-chosen business model not only drives revenue but also builds trust and sustainability across your marketplace ecosystem.
Key Steps to Build a Multi-Seller Marketplace
Building a multi-seller marketplace is a strategic process that brings together business goals, user needs, and technology choices. Instead of overloading the journey with too many phases, focusing on a few critical steps helps accelerate execution while setting the foundation for long-term scalability.

Step 1: Define Your Marketplace Niche and Validate Demand
Every successful marketplace starts with a clear niche and a validated problem. Rather than trying to serve everyone, focus on a specific audience segment where buyers actively seek choice, and sellers need visibility.
Hence, the key areas to focus on:
- Identify your target buyers and sellers
- Understand pain points in existing platforms
- Analyze competitors and gaps in the market
- Validate demand through research, surveys, or early sign-ups
This step reduces risk and ensures your marketplace addresses a real and monetizable problem.
Step 2: Design the Marketplace Business and Revenue Model
Once demand is validated, define how your marketplace will operate and generate revenue. The right business model should support growth while remaining attractive to sellers.
Important considerations:
- Commission structure and pricing strategy
- Subscription, listing, or promotional fee options
- Seller onboarding criteria and platform policies
- Buyer experience and trust mechanisms
A well-planned business model ensures financial sustainability without limiting seller adoption.
Scale up Your Marketplace with Multiple Revenue Streams
Step 3: Define Core Features
Instead of building everything at once, focus on the essential features that enable smooth transactions and trust across the platform for buyers, sellers, and admins.
Key focus areas:
- Seller onboarding, dashboards, and listing management
- Buyer discovery, checkout, and order tracking
- Admin control for commissions, payouts, and moderation
- Mobile responsiveness and performance optimization
- Detailed product or service pages with seller profiles
- Secure checkout with multiple payment options
- Analytics and reporting for sales, users, and platform performance
- Order tracking, notifications, and fulfillment workflows
Launching with a strong MVP allows faster market entry, tests real user behavior, anditeratese confidently as your marketplace grows.
Step 4: Choose the Right Technology Foundation
The technology you choose directly impacts your time-to-market, scalability, and operational complexity. Businesses typically choose between custom development and readymade marketplace software.
Strategic considerations:
- Budget and development timeline
- Customization and scalability needs
- Ongoing maintenance and support
- Ability to adapt as the marketplace grows
Many marketplace founders prefer proven, ready-made solutions to avoid rebuilding complex marketplace logic from scratch and to focus on growth.
Suggested Read: How to Build a Multi-Vendor eCommerce Website from Scratch
Step 5: Launch, Onboard Sellers, and Optimize for Growth
Launching the marketplace marks the beginning of an ongoing growth cycle. Early seller onboarding, quality control, and performance monitoring should be prioritized from day one.
Key activities include:
- Pre-launch seller acquisition and onboarding
- Platform testing and quality assurance
- Marketing and traffic acquisition
- Monitoring performance and user behavior
- Continuous optimization based on data and feedback
Successful marketplaces evolve continuously, improving features, policies, and user experiences as the platform scales.
Marketplace Development Approaches: Build vs Buy
One of the most critical decisions when building a multi-seller marketplace is choosing how the platform will be developed. This choice directly affects your time to market, budget, scalability, and long-term operational complexity.
Broadly, there are two primary approaches to marketplace development:
- Custom marketplace development
- Readymade marketplace software
Each approach has its advantages and limitations. The right choice depends on your business stage, available resources, technical expertise, and growth goals.
1. Custom Marketplace Development
Custom development involves building the marketplace platform entirely from scratch, tailored to specific business requirements. While this approach offers maximum flexibility, it also comes with higher costs, longer timelines, and greater technical risk.
Advantages of Custom Development
- Complete control over features and workflows: Every feature is designed to match your business logic and niche requirements.
- Highly tailored user experience: Ideal for complex or unconventional marketplace models.
- No software dependency: Full ownership of codebase, infrastructure, and future roadmap.
Challenges of Custom Development
- High development cost: Building a marketplace from scratch requires significant upfront investment in design, development, testing, and infrastructure.
- Longer time to market: Development cycles can take anywhere from 6 to 12 months, or longer.
- Ongoing maintenance and upgrades: Continuous investment is required for bug fixes, security patches, and feature enhancements.
- Scalability risks: Poor architectural decisions can limit future growth or require expensive rework later.
Best Suited For
- Enterprises with large budgets and in-house technical teams
- Marketplaces with highly unique workflows or regulatory requirements
- Businesses prioritizing long-term customization over speed
2. Readymade Marketplace Software
Readymade marketplace software provides a pre-built, marketplace-ready foundation that can be customized and branded to suit your business needs. This approach significantly reduces development time and execution risk.
Advantages of Readymade Marketplace Software
- Faster launch and quicker validation: Businesses can go live in weeks rather than months.
- Lower upfront investment: Core marketplace features are already developed and market-tested.
- Proven architecture: These platforms are built using real-world marketplace use cases and refined over time.
- Reduced technical complexity: Less dependency on large development teams or ongoing engineering efforts.
- Easier scalability: Most readymade solutions are designed to handle growth in sellers, products, and transactions.
Challenges to Consider
- Limited flexibility compared to custom builds: Customization depends on the platform’s architecture.
Build vs Buy: Quick Comparison
| Factor | Custom Development | Readymade Software |
| Time to Market | 6-12 months | Few weeks |
| Upfront Cost | High | Predictable & lower |
| Scalability | Depends on the architecture | Built-in |
| Maintenance | High ongoing cost | Vendor-supported |
| Risk Level | High | Lower |
| Ideal For | Large enterprises | Startups & growing businesses |
How to Choose the Right Approach for Your Marketplace
Deciding between custom development and readymade marketplace software is a strategic decision that shapes how quickly you launch, how easily you scale, and how much operational effort you carry. The right approach depends on your priorities today and where you want your marketplace to be in the future. When evaluating your options, consider the following factors:
- Your launch timeline and budget
- Technical expertise and available in-house resources
- Complexity of your marketplace model
- Need for scalability and future upgrades
- Focus on growth vs development effort
For most marketplace founders, especially in early and growth stages, speed, stability, and flexibility outweigh the benefits of fully custom development.
Why Many Businesses Choose Readymade Solutions Like Yo!Kart
As the marketplace ecosystem has matured, many startups and growing businesses now prefer readymade marketplace software to reduce execution risk and accelerate growth.
Solutions like Yo!Kart is designed specifically to support complex multi-seller marketplace operations. Instead of adapting generic eCommerce tools, businesses get workflows, logic, and controls that are native to marketplace models, reducing setup time and operational friction.
Key Benefits:
- Ready-to-Use Seller Onboarding and Management: The platform includes built-in seller registration, approval, and management tools. This allows marketplace owners to onboard vendors quickly, monitor performance, manage listings, and maintain quality standards without relying on custom development.
- Built-In Commission, Subscription, and Payout Systems: Yo!Kart comes with pre-configured monetization features, including commission structures, subscription plans, and automated payout management. These tools help marketplace owners generate revenue efficiently while ensuring transparent and timely settlements for sellers.
- Support for Multiple Marketplace Types: The solution supports a wide range of marketplace models, including product, service, rental, and digital marketplaces. This flexibility allows businesses to adapt or expand their marketplace offerings without rebuilding the platform from scratch.
- White-Label Architecture With Customization Flexibility: Yo!Kart offers a fully white-label framework that can be branded and customized to match specific business requirements. Marketplace owners maintain control over design, workflows, and integrations while preserving a consistent brand identity.
- One-Time License Model With No Recurring Commissions: Unlike commission-based SaaS platforms, Yo!Kart follows a one-time license model. This eliminates recurring commission fees and provides predictable long-term costs, making it easier for businesses to scale without increasing software expenses.
Rather than replacing strategy or innovation, Yo!Kart simplifies complex marketplace operations. This allows businesses to focus on what truly drives success: acquiring sellers, delivering a strong user experience, and scaling the platform with confidence.
Discover How Yo!Kart Powers Marketplaces
Conclusion
Building a multi-seller marketplace is one of the most scalable and future-ready digital business models in today’s economy. However, success requires more than a great idea. It depends on choosing a clear niche, a sustainable revenue model, the right feature set, and, most importantly, a technology foundation that supports growth without adding unnecessary complexity or risk.
While custom development offers flexibility, it often comes with higher costs, longer timelines, and ongoing technical overhead. Hence, for many founders and growing businesses, leveraging readymade marketplace software provides a faster and more cost-efficient path to launch and scale. The key is choosing a solution that is purpose-built for multi-seller operations, flexible enough to adapt as the marketplace evolves, and stable enough to support increasing traffic, sellers, and transactions.
Solutions like Yo!Kart enables marketplace owners to focus on what truly drives long-term success: seller acquisition, user experience, and sustainable growth, rather than rebuilding complex marketplace functionality from scratch. With the right planning and tools in place, launching a scalable multi-seller marketplace becomes a strategic business decision rather than a technical challenge.
FAQs
Q 1. How long does it take to build a multi-seller marketplace?
Ans. The timeline to build a multi-seller marketplace depends on the development approach you select. Marketplaces built using custom development typically take 6-12 months or longer, while readymade marketplace software allows businesses to launch in as little as a few weeks, depending on customization requirements.
Q 2. Can a multi-seller marketplace scale as the business grows?
Ans. Yes, a well-architected multi-seller marketplace can scale in terms of sellers, product listings, traffic, and transactions. Additionally, choosing a scalable platform from the beginning helps avoid costly rebuilds as the marketplace expands.
Q 3. Is technical expertise required to run a marketplace platform?
Ans. Not necessarily, day-to-day operations do not require deep technical expertise when using modern marketplace software. Most modern marketplace solutions provide admin dashboards, automation, and support tools that allow non-technical teams to manage sellers, orders, and payments efficiently.
Q 4. How do multi-seller marketplaces make money?
Ans. Multi-seller marketplaces typically earn revenue through commissions on transactions, seller subscription plans, listing fees, featured placements, or a combination of these monetization models. However, the right mix depends on your marketplace type, audience, and long-term growth strategy.
Q 5. Is readymade marketplace software a good option for US-based startups?
Ans. Yes, for many US-based startups and SMBs, readymade marketplace software is a good option. It offers faster time-to-market, predictable costs, and reduced technical risk compared to custom development, making it an effective option for validating and scaling marketplace ideas.



