Published Date 23rd Dec, 2025
Multi-vendor eCommerce marketplaces are reshaping the way digital commerce operates. As we move toward 2026, the marketplace model has evolved from being a disruptive alternative to becoming a dominant, preferred approach for selling products, services, and digital experiences online.
Unlike traditional eCommerce stores that rely on inventory ownership and linear growth, multi-vendor marketplaces thrive on ecosystems. They connect multiple sellers with buyers across the globe on a single platform, enabling platforms to scale faster, diversify revenue, and adapt to market changes without rebuilding from scratch.
In this detailed blog, you will explore the most popular multi-vendor eCommerce business models to watch in 2026, why they are growing, how they make money, and what entrepreneurs should consider before launching their own marketplace.
Table of Contents
Why Multi-Vendor Marketplaces Are Dominating in 2026?
Before diving into individual business models, it’s important to understand why marketplaces continue to outperform traditional eCommerce. The shift toward marketplaces is not driven by a trend alone, but by structural advantages that align better with how modern commerce operates. As consumer behavior, seller expectations, and technology continue to evolve, marketplaces offer a more sustainable and future-ready path than single-seller eCommerce models.
1. Scalable, Inventory-Free Growth
Marketplace owners are not required to invest in inventory, storage, warehouses, or logistics infrastructure. Vendors handle supply independently, allowing the platform to focus on demand, technology, and trust.
2. Self-Reinforcing Growth Dynamics
Each new seller increases product variety, which attracts more buyers. More buyers, in turn, attract more sellers. This compounding growth is difficult for single-seller stores to replicate.
3. Multiple Monetization Streams
Unlike traditional stores that rely primarily on product margins, Marketplaces are not limited to one revenue source. Generally, they diversify income through commissions, subscriptions, listings, ads, and premium services.
4. Faster Market Expansion
Marketplaces can introduce new categories, services, or regions with minimal operational friction. This flexibility allows founders to test new verticals, pivot strategies, and respond quickly to market demand.
5. Changing Seller Expectations
Brands, manufacturers, and independent sellers increasingly prefer platforms with built-in traffic, trust signals, and operational tools rather than investing time and capital into standalone stores.
Best Multi-Vendor eCommerce Business Models
Multi-vendor marketplaces do not follow a one-size-fits-all approach. Some marketplaces win by offering unmatched variety, while others succeed through deep specialization, local relevance, or service-driven experiences. Understanding how each model works, where it excels, and what it demands operationally is essential before choosing the right path for your marketplace. Let’s have a look at some of the best multi-vendor eCommerce business models:
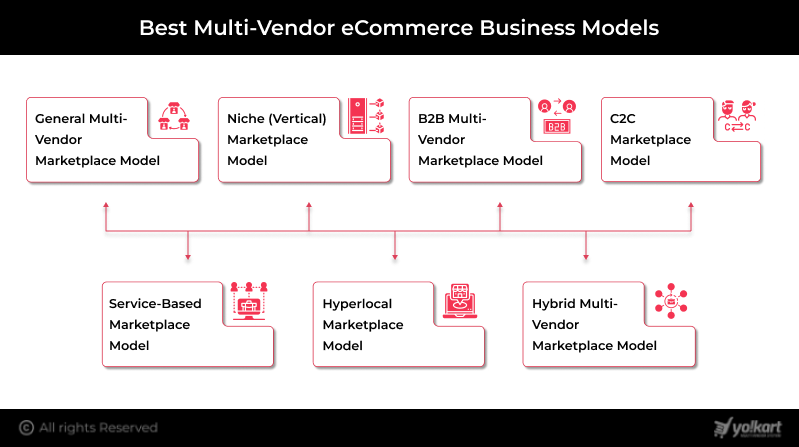
1. General (Horizontal) Multi-Vendor Marketplace Model
A horizontal marketplace allows sellers from multiple categories to sell on one platform. These marketplaces prioritize volume, convenience, and product variety, allowing buyers to find almost anything in one place. Rather than specialization, they compete on reach, logistics strength, and discovery capabilities.
Why It Still Matters in 2026
Despite the rise of niche platforms, general or horizontal marketplaces remain relevant due to:
- One-stop shopping convenience
- Strong brand recognition
- Advanced personalization and AI-driven product discovery
Key Highlights
- Wide product assortment
- Large seller base
- High traffic potential
- Strong logistics integrations
Revenue Models
- Commission per transaction
- Sponsored listings
- Vendor subscription plans
Examples:
1. Amazon Marketplace
Amazon allows third-party sellers to list products alongside Amazon’s own inventory. Its success lies in massive buyer traffic, strong logistics, and advanced recommendation engines.
2. eBay
A pioneer of multi-vendor commerce, eBay supports auctions and fixed-price listings across countless categories, including new, used, and collectible products.
3. Walmart Marketplace
Walmart’s marketplace focuses on curated sellers and strong fulfillment support, blending online and offline retail experiences.
Suggested Read: How to Build Horizontal B2B Marketplaces
Launch Your Own Amazon-Like Marketplace
2. Niche (Vertical) Marketplace Model
Niche or Vertical marketplaces are built around a single niche or industry, such as fashion, automotive parts, handmade goods, industrial equipment, or sustainable products. Instead of trying to serve everyone, these platforms focus on depth, relevance, and expertise, delivering tailored experiences that broad marketplaces often cannot match.
Why Niche Marketplaces Are Exploding
In 2026, buyers increasingly value expertise over variety. Niche marketplaces succeed by solving specific problems better than broad platforms.
Key Highlights
- Higher trust and loyalty
- Better seller quality
- Easier differentiation
- Higher conversion rates
Popular Niche Categories
- Auto aftermarket & spare parts
- Health & wellness equipment
- Sustainable and eco-friendly products
- B2B industrial supplies
- Creator and handmade goods
Revenue Models
- Commission
- Premium vendor memberships
- Category-specific promotions
Best Suited For
Founders with domain expertise or access to underserved or fragmented markets.
Examples:
1. Etsy
A global marketplace dedicated to handmade, vintage, and creative goods. Etsy thrives on community trust and creator-driven commerce.
2. StockX
A niche marketplace focused on sneakers, streetwear, and collectibles, using authentication and resale pricing to build trust.
3. Reverb
A vertical marketplace dedicated to musical instruments and gear, catering specifically to musicians and professional sellers with industry-specific tools.
Suggested Read: How to Build a Vertical Marketplace?
3. B2B Multi-Vendor Marketplace Model
B2B marketplaces connect manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, and institutional buyers on a digital procurement platform. These marketplaces are designed to streamline complex buying processes, reduce sourcing friction, and support high-value transactions between businesses.
Why B2B Marketplaces Will Lead in Value
By 2026, B2B eCommerce is expected to surpass B2C in transaction value due to:
- Bulk and repeat purchasing
- Long-term seller and buyer contracts
- Digital transformation of procurement
Key Highlights
- Large order sizes
- Negotiation and RFQ workflows
- Custom pricing and credit terms
- Account-based buying
Revenue Models
- Vendor subscriptions
- Commission on transactions
- Premium enterprise tools
Best Suited For
Industry aggregators, manufacturers, and enterprise-focused startups or wholesale commerce.
Examples:
1. Alibaba
A global B2B marketplace connecting manufacturers and wholesalers with buyers worldwide, especially for large-volume sourcing.
2. Thomasnet
A US-based B2B platform that helps industrial buyers discover and connect with verified manufacturers and suppliers.
3. Faire
A wholesale marketplace that connects independent retailers with brands, simplifying B2B ordering and payments.
Suggested Read: B2B Marketplace Development: Everything You Need to Know
4. C2C (Peer-to-Peer) Marketplace Model
C2C marketplaces enable individuals to sell directly to other individuals. These platforms thrive on community, trust, and ease of use. Further, they remove traditional retail barriers, making it easy for anyone to become a seller.
Why C2C Keeps Growing
Trends such as sustainability, resale culture, and creator economies are pushing peer-to-peer commerce forward.
Key Highlights
- Low seller onboarding barriers
- Strong community engagement
- Review-driven trust systems
Popular Use Cases
- Pre-owned goods
- Handmade products
- Collectibles
- Digital assets
Revenue Models
- Listing fees
- Transaction commissions
- Featured placements
Examples:
1. Facebook Marketplace
A community-driven platform that enables local buying and selling, benefiting from social trust and ease of access.
2. OfferUp
A US-based peer-to-peer marketplace focused on local resale, offering a mobile-first experience for used goods.
3. Depop
A fashion-focused peer-to-peer marketplace popular among younger audiences and resale communities.
Suggested Read: How to Build C2C Marketplace
5. Service-Based Marketplace Model
Service marketplaces connect buyers with professionals offering services instead of products. These platforms support a wide range of providers, including tutors, consultants, freelancers, technicians, and wellness professionals, making it easier for customers to find and book trusted expertise on demand.
Why Service Marketplaces Are Booming
Consumers increasingly prefer convenient, on-demand access to verified professionals, along with transparent pricing and scheduling.
Key Highlights
- Time-based or package-based bookings
- Vendor availability management
- Ratings and reviews
Use Cases
- Online tutoring platforms
- Home services marketplaces
- Professional consulting platforms
Revenue Models
- Commission per booking
- Subscription plans
- Lead generation fees
Examples:
1. Upwork
A global freelance marketplace connecting businesses with professionals offering digital and creative services.
2. Fiverr
A service marketplace built around packaged offerings, enabling freelancers to sell predefined services.
3. Thumbtack:
A US-based marketplace that connects consumers with local service professionals for home, repair, and personal services.
6. Hyperlocal Marketplace Model
Hyperlocal marketplaces focus on local sellers and nearby buyers, often emphasizing speed and convenience. These platforms are especially effective for time-sensitive purchases where quick fulfillment and local availability matter more than broad selection.
Why Hyperlocal Matters in 2026
Urbanization and consumer demand for fast delivery drive hyperlocal commerce — especially for groceries, essentials, and services.
Key Highlights
- Location-based discovery
- Same-day or instant delivery
- Strong local seller relationships
Revenue Models
- Commission
- Delivery fees
- Vendor subscriptions
Examples:
1. Instacart
A grocery marketplace connecting customers with local stores for fast and same-day delivery.
2. Dunzo
A hyperlocal delivery marketplace enabling users to order groceries, food, and essentials from nearby stores through a hyperlocal network.
3. Postmates
A local delivery marketplace offering food, groceries, and essentials from nearby vendors.
7. Hybrid Multi-Vendor Marketplace Model
Hybrid marketplaces combine multiple business models within a single platform, allowing them to serve diverse user needs and evolve over time. Common hybrid combinations include:
- B2C + C2C
- Products + services
- Online + offline
Why Hybrid Models Are the Future
Most successful marketplaces do not remain static. As they grow, they expand into new categories, add services, or introduce new seller types. Hybrid models enable this evolution without the need to rebuild or migrate platforms.
Key Highlights
- Flexible monetization
- Long-term scalability
- Future-proof architecture
Examples:
1. Walmart:
Evolved from a traditional retailer into a hybrid marketplace supporting third-party sellers, omnichannel fulfillment, and private labels.
2. Etsy (Hybrid Evolution)
Combines a core C2C marketplace with B2C sellers, digital products, and value-added services for creators.
3. Amazon (Hybrid Model)
Amazon operates as a retailer, marketplace, logistics provider, and service platform simultaneously.
Launch a Hybrid Marketplace Designed for Long-Term Growth
Popular Niches to Launch a Marketplace in 2026
Choosing the right niche is one of the most critical success factors for any multi-vendor marketplace. Today, the most successful marketplaces are highly focused, solve specific problems, and serve clearly defined audiences.
Rather than competing head-on with global giants, new marketplace founders are finding success by targeting underserved industries, fragmented supply chains, and experience-driven communities built around shared interests or experiences. Below are some of the most promising marketplace niches to launch in 2026, and the reasons they continue to gain momentum.

1. Auto Parts & Aftermarket Accessories
The global automotive aftermarket continues to grow as vehicle ownership cycles lengthen and customization becomes mainstream. Buyers increasingly look for specialized platforms that make it easy to find the right parts for their vehicles.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- Strong repeat purchase behavior
- Highly fragmented supplier base
- Growing demand for customization and replacement parts
Marketplace opportunities:
- Vehicle-specific product discovery
- OEM vs aftermarket comparison
- B2C and B2B hybrid selling
This niche benefits greatly from advanced filtering, vendor specialization, and long-tail product listings.
2. B2B Industrial & Spare Parts Marketplaces
Industrial procurement is rapidly moving online, but many industries still rely on outdated offline sourcing methods. This creates a strong opportunity for specialized B2B marketplaces.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- High-order values
- Recurring procurement cycles
- Low competition compared to B2C
Marketplace opportunities:
- RFQ-based buying
- Vendor certifications and compliance
- Custom pricing and bulk ordering
These marketplaces prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and trust over visual merchandising.
3. Sustainable & Eco-Friendly Products
Sustainability is no longer optional. Consumers actively seek marketplaces that align with ethical and environmental values, making this niche increasingly attractive.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- Rising eco-conscious consumer base
- Strong brand loyalty
- Premium pricing potential
Marketplace opportunities:
- Certified eco-vendors
- Transparent sourcing information
- Subscription-based replenishment models
Niche sustainability marketplaces often outperform generic platforms on engagement and retention.
4. Health, Wellness & Fitness Equipment
Health-focused spending continues to rise, driven by preventive care, home fitness, and wellness lifestyles. Buyers increasingly expect expert guidance, credible brands, and evidence-backed product information when making purchase decisions.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- Expanding global health awareness
- Growth of home-based fitness
- High-value product segments
Marketplace opportunities:
- Expert-led product recommendations
- Service + product hybrid models
- Community-driven reviews
Trust, credibility, and high-quality content play a major role in success within this niche.
5. Education, Tutoring & Skill-Based Marketplaces
Learning is increasingly modular, digital, and outcome-driven. Marketplaces that connect learners with qualified educators and practical skills are seeing sustained global demand.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- Lifelong learning is becoming standard
- Rising demand for personalized education
- Strong global reach
Marketplace opportunities:
- Tutor and course marketplaces
- Skill-based service listings
- Subscription and package pricing
This niche often blends products, services, and digital content into a single learning ecosystem.
6. Local Services & Hyperlocal Commerce
Consumers value speed, proximity, and community trust, making hyperlocal platforms highly relevant. Moreover, hyperlocal platforms succeed by reducing friction and delivering reliable, location-specific experiences.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- Urbanization and local commerce revival
- Demand for same-day or instant services
- Support for local businesses
Marketplace opportunities:
- Home services and repairs
- Local professional services
- Geo-based vendor discovery
Hyperlocal marketplaces depend heavily on location intelligence and operational efficiency.
7. Handmade, Creator & Community Marketplaces
The creator economy continues to expand, driven by independent makers and small brands. These marketplaces emphasize storytelling, craftsmanship, and community-driven engagement.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- Shift toward authenticity and personalization
- Strong community-driven purchasing
- Social commerce integration
Marketplace opportunities:
- Artist and artisan platforms
- Limited-edition product drops
- Direct-to-fan monetization
These platforms thrive on storytelling, trust, and community engagement.
8. Digital Products & Subscription Marketplaces
Digital goods eliminate logistics complexity while offering high margins. They appeal to creators and businesses looking to monetize expertise, tools, and content globally.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- Zero inventory and shipping costs
- Instant fulfillment
- Global scalability
Marketplace opportunities:
- Software, plugins, templates
- Digital art and content
- Membership and subscription access
This niche benefits from automation, secure delivery, and recurring revenue models.
9. Experience & Activity Marketplaces
Consumers increasingly value experiences that offer personal enrichment, entertainment, or learning over ownership. These marketplaces connect users with memorable, time-based activities.
Why this niche works in 2026:
- Growth of experiential spending
- Tourism and local experiences rebounding
- Service-based monetization
Marketplace opportunities:
- Travel activities and tours
- Workshops and events
- Time-slot-based bookings
Experience marketplaces rely on availability management and trust signals to succeed.
Transform Your Niche Idea Into a Fully Functional Marketplace
Building a Marketplace: Key Considerations for 2026
Launching a successful multi-vendor marketplace in 2026 requires more than just listing products or services online. Today’s marketplaces succeed because they solve real problems, provide exceptional user experiences, and leverage the right technology. Before launching, founders must make informed decisions that shape both short-term traction and long-term growth. Here’s what every founder should consider:
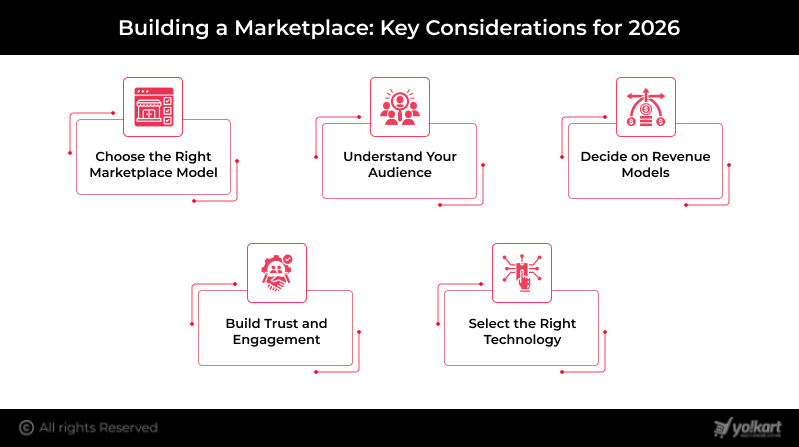
1. Choose the Right Marketplace Model
Your marketplace model defines how your platform operates, grows, and generates revenue. Selecting the right structure early helps avoid costly pivots later.
Popular business models include:
- Horizontal Marketplaces: Wide product range, high marketing demands
- Vertical/Niche Marketplaces: Specialized categories, higher conversion rates
- B2B Marketplaces: Bulk orders, long-term client relationships
- C2C & Service Marketplaces: Focused on trust, ease of use, and community
- Hybrid Marketplaces: Combine models for flexibility and growth
2. Understand Your Audience
Every successful marketplaces start with clarity about who buys and who sells. Thus, you should:
- Define the needs and pain points of buyers
- Identify the type of vendors that can meet those needs
- Map the user journey for both buyers and sellers
3. Decide on Revenue Models
Marketplaces benefit from flexible monetization, but the right mix depends on your niche and audience. However, common monetization options include:
- Transaction-based commissions
- Seller subscriptions or membership plans
- Featured listings, advertising, or premium services
- Combination models tailored to your niche
Choosing the right revenue strategy early ensures long-term profitability while keeping sellers engaged.
4. Build Trust and Engagement
Trust is the foundation of any marketplace ecosystem. Without it, growth and retention suffer. Thus, to build trust, you should:
- Implement ratings and reviews for sellers
- Provide transparent dispute resolution
- Ensure quality control across vendors
A trusted marketplace drives repeat purchases, higher engagement, and vendor retention.
5. Select the Right Technology
Technology is the backbone of marketplace success and scalability. Founders must ensure their platform can:
- Scale seamlessly with more vendors and buyers
- Adapt to different business models (B2B, B2C, hybrid, service-based)
- Handle payments securely and integrate logistics efficiently
- Offer analytics dashboards for vendor and platform performance
Choosing the right technology not only accelerates launch but also ensures your marketplace can grow and evolve over time.
Why Yo!Kart is the Right Choice for Your Marketplace?
Once your marketplace model and strategy are clearly defined, the next critical decision is choosing a technology foundation that can support both your immediate launch and long-term growth. The right solution reduces time to market, minimizes technical risk, and gives you the flexibility to evolve as your business matures.
One such solution is Yo!Kart is a purpose-built multi-vendor software that meets these demands, offering a stable, enterprise-grade foundation. It allows founders to focus on growth, partnerships, and customer experience rather than rebuilding core systems. Moreover, this robust solution comes pre-integrated with APIs, essential features, and readymade mobile apps for buyers (Android and iOS). Let’s have a look at the advantages offered by Yo!Kart:
1. Built for Multi-Vendor Marketplaces
Yo!Kart’s is designed specifically for multi-vendor commerce, supporting B2C, B2B, C2C, and hybrid models, along with native vendor management and flexible commission structures. This makes it easier to launch any type of marketplace without reengineering core functionality.
2. Scalable and Future-Ready
Unlike many SaaS platforms with traffic or transaction caps, Yo!Kart scale with your growth. The self-hosted architecture removes artificial limits on traffic or transactions, allowing you to expand categories, onboard large vendor networks, and enter new markets without performance bottlenecks.
3. Customizable Workflows and Features
Every niche has unique requirements. Therefore, Yo!Kart allows:
- Industry-specific product attributes
- Custom pricing and vendor policies
- Integrations with payment gateways, shipping partners, and marketing tools
4. Cost-Effective Ownership
Yo!Kart offers a one-time license fee, eliminating recurring revenue-sharing or subscription costs. Founders retainfull ownership of the platform and source code, providing predictable costs and long-term control over the business.
5. Supports Long-Term Evolution
Marketplaces often evolve from niche-focused to hybrid or multi-category models. Yo!Kart is built to support gradual evolution, whether you expand into new categories, introduce services, or transition into a hybrid model. This adaptability ensures your technology investment continues to deliver value as your marketplace grows and changes over time.
Suggested Read: How to Build C2C Marketplace
Conclusion
The multi-vendor marketplace landscape is evolving rapidly, and 2026 will be defined by specialization, hybrid business models, and technology-driven scalability. Whether you are launching a niche marketplace, a B2B platform, a C2C resale hub, or a service-based ecosystem, long-term success depends on aligning the right business model with your target audience, fostering trust and transparency, and creating meaningful engagement across your community. Purpose-built multi-vendor marketplace software like Yo!Kart empowers founders to launch efficiently, scale without constraints, and adapt to emerging market trends. By combining strategic planning, niche focus, and the right technology foundation, your marketplace can not only compete but thrive in the increasingly competitive eCommerce ecosystem. When built thoughtfully, a marketplace becomes more than a transaction layer. It becomes a long-term digital asset that connects sellers, buyers, and experiences in a sustainable and scalable way.